Prediction of COVID-19 with Computed Tomography Images using Hybrid Learning Techniques
- PMID: 33968281
- PMCID: PMC8063851
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/5522729
Prediction of COVID-19 with Computed Tomography Images using Hybrid Learning Techniques
Abstract
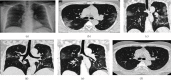
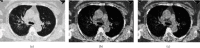
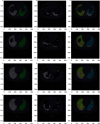
Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR) used for diagnosing COVID-19 has been found to give low detection rate during early stages of infection. Radiological analysis of CT images has given higher prediction rate when compared to RT-PCR technique. In this paper, hybrid learning models are used to classify COVID-19 CT images, Community-Acquired Pneumonia (CAP) CT images, and normal CT images with high specificity and sensitivity. The proposed system in this paper has been compared with various machine learning classifiers and other deep learning classifiers for better data analysis. The outcome of this study is also compared with other studies which were carried out recently on COVID-19 classification for further analysis. The proposed model has been found to outperform with an accuracy of 96.69%, sensitivity of 96%, and specificity of 98%.
Copyright © 2021 Varalakshmi Perumal et al.
Conflict of interest statement
On behalf of all the authors, the corresponding author state that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Automated system for classification of COVID-19 infection from lung CT images based on machine learning and deep learning techniques.Sci Rep. 2022 Oct 18;12(1):17417. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-20804-5. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36257964 Free PMC article.
-
Large-scale screening to distinguish between COVID-19 and community-acquired pneumonia using infection size-aware classification.Phys Med Biol. 2021 Mar 17;66(6):065031. doi: 10.1088/1361-6560/abe838. Phys Med Biol. 2021. PMID: 33729998
-
Assisting scalable diagnosis automatically via CT images in the combat against COVID-19.Sci Rep. 2021 Feb 18;11(1):4145. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-83424-5. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33603047 Free PMC article.
-
Thoracic imaging tests for the diagnosis of COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Nov 26;11:CD013639. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013639.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Mar 16;3:CD013639. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013639.pub4. PMID: 33242342 Updated.
-
The Limited Sensitivity of Chest Computed Tomography Relative to Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction for Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus-2 Infection: A Systematic Review on COVID-19 Diagnostics.Invest Radiol. 2020 Dec;55(12):754-761. doi: 10.1097/RLI.0000000000000700. Invest Radiol. 2020. PMID: 32554983 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Using fused Contourlet transform and neural features to spot COVID19 infections in CT scan images.Intell Syst Appl. 2023 Feb;17:200182. doi: 10.1016/j.iswa.2023.200182. Epub 2023 Jan 13. Intell Syst Appl. 2023. PMID: 40478143 Free PMC article.
-
Review and classification of AI-enabled COVID-19 CT imaging models based on computer vision tasks.Comput Biol Med. 2022 Feb;141:105123. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2021.105123. Epub 2021 Dec 18. Comput Biol Med. 2022. PMID: 34953356 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Deep-Learning-Based COVID-19 Diagnosis and Implementation in Embedded Edge-Computing Device.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Apr 3;13(7):1329. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13071329. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37046553 Free PMC article.
-
CVD-HNet: Classifying Pneumonia and COVID-19 in Chest X-ray Images Using Deep Network.Wirel Pers Commun. 2022;126(4):3279-3303. doi: 10.1007/s11277-022-09864-y. Epub 2022 Jun 19. Wirel Pers Commun. 2022. PMID: 35756172 Free PMC article.
-
Learning without forgetting by leveraging transfer learning for detecting COVID-19 infection from CT images.Sci Rep. 2023 May 25;13(1):8516. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-34908-z. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37231044 Free PMC article.
References
-
- WHO. Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Situation Report–39. World Health Organization; 2020.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

