Plasma Small Extracellular Vesicle-Carried miRNA-501-5p Promotes Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Phenotypic Modulation-Mediated In-Stent Restenosis
- PMID: 33968296
- PMCID: PMC8084657
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/6644970
Plasma Small Extracellular Vesicle-Carried miRNA-501-5p Promotes Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Phenotypic Modulation-Mediated In-Stent Restenosis
Abstract
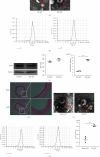
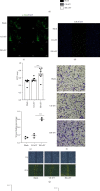
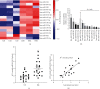
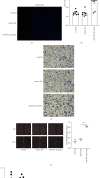
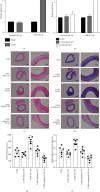
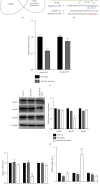
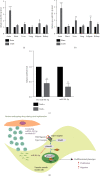
Vascular smooth muscle cell (VSMC) phenotypic modulation plays an important role in the occurrence and development of in-stent restenosis (ISR), the underlying mechanism of which remains a key issue needing to be urgently addressed. This study is designed to investigate the role of plasma small extracellular vesicles (sEV) in VSMC phenotypic modulation. sEV were isolated from the plasma of patients with ISR (ISR-sEV) or not (Ctl-sEV) 1 year after coronary stent implantation using differential ultracentrifugation. Plasma sEV in ISR patients are elevated markedly and decrease the expression of VSMC contractile markers α-SMA and calponin and increase VSMC proliferation. miRNA sequencing and qRT-PCR validation identified that miRNA-501-5p was the highest expressed miRNA in the plasma ISR-sEV compared with Ctl-sEV. Then, we found that sEV-carried miRNA-501-5p level was significantly higher in ISR patients, and the level of plasma sEV-carried miRNA-501-5p linearly correlated with the degree of restenosis (R 2 = 0.62). Moreover, miRNA-501-5p inhibition significantly increased the expression of VSMC contractile markers α-SMA and calponin and suppressed VSMC proliferation and migration; in vivo inhibition of miRNA-501-5p could also blunt carotid artery balloon injury induced VSMC phenotypic modulation in rats. Mechanically, miRNA-501-5p promoted plasma sEV-induced VSMC proliferation by targeting Smad3. Notably, endothelial cells might be the major origins of miRNA-501-5p. Collectively, these findings showed that plasma sEV-carried miRNA-501-5p promotes VSMC phenotypic modulation-mediated ISR through targeting Smad3.
Copyright © 2021 Xiao-Fei Gao et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that no conflict of interest exists.
Figures
Similar articles
-
microRNA-18a-5p promotes vascular smooth muscle cell phenotypic switch by targeting Notch2 as therapeutic targets in vein grafts restenosis.Eur J Pharmacol. 2024 Dec 15;985:177097. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2024.177097. Epub 2024 Nov 8. Eur J Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39522684
-
miRNA‑92a inhibits vascular smooth muscle cell phenotypic modulation and may help prevent in‑stent restenosis.Mol Med Rep. 2023 Feb;27(2):40. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2023.12927. Epub 2023 Jan 5. Mol Med Rep. 2023. PMID: 36601739 Free PMC article.
-
NONRATT000538.2 promotes vascular smooth muscle cell phenotypic switch and in-stent restenosis.Exp Cell Res. 2024 Oct 1;442(2):114260. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2024.114260. Epub 2024 Sep 18. Exp Cell Res. 2024. PMID: 39303839
-
The microRNAs Regulating Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Proliferation: A Minireview.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jan 14;20(2):324. doi: 10.3390/ijms20020324. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30646627 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An overview of potential molecular mechanisms involved in VSMC phenotypic modulation.Histochem Cell Biol. 2016 Feb;145(2):119-30. doi: 10.1007/s00418-015-1386-3. Epub 2015 Dec 26. Histochem Cell Biol. 2016. PMID: 26708152 Review.
Cited by
-
Extracellular Vesicles as Drivers of Immunoinflammation in Atherothrombosis.Cells. 2022 Jun 5;11(11):1845. doi: 10.3390/cells11111845. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35681540 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNA regulation of phenotypic transformations in vascular smooth muscle: relevance to vascular remodeling.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2023 May 10;80(6):144. doi: 10.1007/s00018-023-04793-w. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2023. PMID: 37165163 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Restenosis after Coronary Stent Implantation: Cellular Mechanisms and Potential of Endothelial Progenitor Cells (A Short Guide for the Interventional Cardiologist).Cells. 2022 Jun 30;11(13):2094. doi: 10.3390/cells11132094. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35805178 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular Non-Coding RNAs in Cardiovascular Diseases.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Jan 3;15(1):155. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15010155. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 36678784 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Cardiac Troponin and Other Emerging Biomarkers Among Athletes and Beyond: Underlying Mechanisms, Differential Diagnosis, and Guide for Interpretation.Biomolecules. 2024 Dec 19;14(12):1630. doi: 10.3390/biom14121630. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39766337 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Gao X.-F., Lu S., Ge Z., et al. Relationship between high platelet reactivity on clopidogrel and long-term clinical outcomes after drug-eluting stents implantation (PAINT-DES): a prospective, propensity score-matched cohort study. BMC Cardiovascular Disorders. 2018;18(1):p. 103. doi: 10.1186/s12872-018-0841-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gao X.-F., Kan J., Zhang Y.-J., et al. Comparison of one-year clinical outcomes between intravascular ultrasound-guided versus angiography-guided implantation of drug-eluting stents for left main lesions: a single-center analysis of a 1,016-patient cohort. Patient Preference and Adherence. 2014;8:1299–1309. doi: 10.2147/PPA.S65768. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

