Hepatic Manifestations of Inflammatory Bowel Disease
- PMID: 33968391
- PMCID: PMC8087932
- DOI: 10.1002/cld.1046
Hepatic Manifestations of Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Figures

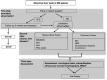
References
-
- Mendes FD, Levy C, Enders FB, et al. Abnormal hepatic biochemistries in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Am J Gastroenterol 2007;102:344‐350. - PubMed
-
- Chapman R, Fevery J, Kalloo A, et al. Diagnosis and management of primary sclerosis cholangitis. Hepatology 2010;51:660‐678. - PubMed
-
- Restellini S, Chazouillères O, Frossard JL. Hepatic manifestations of inflammatory bowel diseases. Liver Int 2017;37:475‐489. - PubMed
-
- European Association for the Study of the Liver . EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines: management of cholestatic liver diseases. J Hepatol 2009;51:237‐267. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

