One-year intradialytic leg exercises with resistance bands and fat mass increase in elderly hemodialysis patients: a retrospective study
- PMID: 33968420
- PMCID: PMC8097127
- DOI: 10.1186/s41100-021-00341-z
One-year intradialytic leg exercises with resistance bands and fat mass increase in elderly hemodialysis patients: a retrospective study
Abstract
Background: Intradialytic exercises are recommended to be available as a treatment for enhancing physical functioning. However, there have been few reports which evaluated the results of long-term mild intradialytic exercises in elderly patients. The purpose of this study is to investigate the changes in body weight, body composition, and laboratory data in elderly hemodialysis patients after 1-year intradialytic leg exercises with resistance bands.
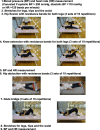
Methods: A retrospective study. Twenty-one outpatients, aged 65 or older (mean ± SD, 75.2 ± 5.1 years), received intradialytic leg exercises with resistance bands for a year were analyzed. The values of dry weight, body composition, and laboratory data were collected from the year-ago period, at baseline and 1 year after baseline. Fat and muscle mass were evaluated by using a multi-frequency bioimpedance device.
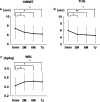
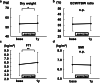
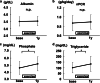
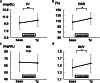
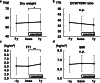
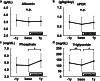
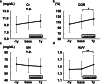
Results: Physical performance changed and body weight increased after 1-year resistance band exercises. However, the participants gained fat mass, not muscle mass. Although the changes in biochemical data related to protein intake were equivocal, triglyceride levels increased significantly after 1-year exercises. An elevation in serum creatinine levels was observed, even if solute clearance increased significantly.
Conclusions: One-year intradialytic leg exercises with resistance bands may have a potential clinical benefit for body mass index even in elderly hemodialysis patients. However, optimal dietary modification is needed to achieve a balanced increase of muscle and fat mass. An increase of serum creatinine levels does not always mean muscle mass hypertrophy.
Supplementary information: The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1186/s41100-021-00341-z.
Keywords: Body composition; Dialysis; Multi-frequency bioimpedance; Nutrition; Resistance exercise.
© The Author(s) 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsNone.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Intradialytic Resistance Training Improves Functional Capacity and Lean Mass Gain in Individuals on Hemodialysis: A Randomized Pilot Trial.Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2019 Nov;100(11):2151-2158. doi: 10.1016/j.apmr.2019.06.006. Epub 2019 Jul 3. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2019. PMID: 31278924 Clinical Trial.
-
Intradialytic exercise improves physical function and reduces intradialytic hypotension and depression in hemodialysis patients.Korean J Intern Med. 2019 May;34(3):588-598. doi: 10.3904/kjim.2017.020. Epub 2017 Aug 25. Korean J Intern Med. 2019. PMID: 28838226 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The effects of exercise during hemodialysis on physical performance and nutrition assessment.J Ren Nutr. 1999 Apr;9(2):63-70. doi: 10.1016/s1051-2276(99)90002-x. J Ren Nutr. 1999. PMID: 10089261 Clinical Trial.
-
The effects of intradialytic exercise on hemodialysis adequacy: A systematic review.Semin Dial. 2019 Jul;32(4):368-378. doi: 10.1111/sdi.12785. Epub 2019 Apr 9. Semin Dial. 2019. PMID: 30968465
-
A Comparison of Intradialytic versus Out-of-Clinic Exercise Training Programs for Hemodialysis Patients.Blood Purif. 2020;49(1-2):151-157. doi: 10.1159/000503772. Epub 2019 Dec 18. Blood Purif. 2020. PMID: 31851985 Review.
References
-
- Ashby D, Borman N, Burton J, Corbett R, Davenport A, Farrington K, Flowers K, Fotheringham J, Andrea Fox RN, Franklin G, Gardiner C, Martin Gerrish RN, Greenwood S, Hothi D, Khares A, Koufaki P, Levy J, Lindley E, Macdonald J, Mafrici B, Mooney A, Tattersall J, Tyerman K, Villar E, Wilkie M. Renal association clinical practice guideline on haemodialysis. BMC Nephrol. 2019;20(1):379. doi: 10.1186/s12882-019-1527-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Martin-Alemañy G, Espinosa-Cuevas MLÁ, Pérez-Navarro M, Wilund KR, Miranda-Alatriste P, Cortés-Pérez M, et al. Effect of oral nutritional supplementation with and without exercise on nutritional status and physical function of adult hemodialysis patients: a parallel controlled clinical trial (AVANTE-HEMO Study) J Ren Nutr. 2020;30(2):126–136. doi: 10.1053/j.jrn.2019.06.010. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
