Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis as a Cause of Sudden-Onset Bilateral Sensorineural Hearing Loss: Case Report and Recommendations for Initial Assessment
- PMID: 33968458
- PMCID: PMC8081636
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/6632344
Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis as a Cause of Sudden-Onset Bilateral Sensorineural Hearing Loss: Case Report and Recommendations for Initial Assessment
Abstract
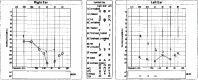
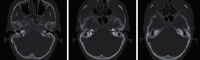
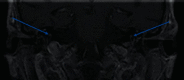
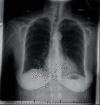
Granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA) is a severe systemic vasculitis that commonly affects the paranasal sinuses, upper and lower respiratory tracts, and kidneys. GPA has also been associated with sensorineural hearing loss (SNHL), through inflammation of the cochlear apparatus. Early recognition, diagnostic laboratory evaluation, and appropriate treatment are essential to improve outcomes and achieve remission for patients with GPA. Here, we present a case of bilateral sudden sensorineural hearing loss (SSNHL) and distal symmetric polyneuropathy as the first presenting signs of GPA. A specific diagnostic work-up to rule out autoimmune inner-ear disease in patients with bilateral SSNHL is not clearly stated in the clinical practice guidelines from the American Academy of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery. The aim of this paper is to delineate an appropriate diagnostic work-up for patients with bilateral SSNHL when there is concern for autoimmune disease.
Copyright © 2021 Paul R. Ratmeyer et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Atypical presentation of granulomatosis with polyangiitis: a case report and review of the literature.AME Case Rep. 2024 Jul 4;8:82. doi: 10.21037/acr-24-47. eCollection 2024. AME Case Rep. 2024. PMID: 39091557 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Practice Guideline: Sudden Hearing Loss (Update).Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2019 Aug;161(1_suppl):S1-S45. doi: 10.1177/0194599819859885. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2019. PMID: 31369359
-
Clinical Practice Guideline: Sudden Hearing Loss (Update) Executive Summary.Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2019 Aug;161(2):195-210. doi: 10.1177/0194599819859883. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2019. PMID: 31369349
-
Clinic manifestations in granulomatosis with polyangiitis.Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2016 Jun;29(2):151-9. doi: 10.1177/0394632015617063. Epub 2015 Dec 18. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 26684637 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Granulomatosis With Polyangiitis in Otolaryngologist Practice: A Review of Current Knowledge.Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol. 2016 Mar;9(1):8-13. doi: 10.21053/ceo.2016.9.1.8. Epub 2016 Mar 7. Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol. 2016. PMID: 26976020 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Clinical characteristics of patients diagnosed with bilateral sudden sensorineural hearing loss.Front Neurol. 2024 Jun 24;15:1378017. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1378017. eCollection 2024. Front Neurol. 2024. PMID: 38978810 Free PMC article.
-
Granulomatosis with polyangiitis presenting as isolated ear involvement: a case series and literature review.Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital. 2025 Jun;45(3):217-230. doi: 10.14639/0392-100X-N3008. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital. 2025. PMID: 40567100 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Weirzbica M., Szyfter W., Puszczewicz M., et al. Otologic symptoms as initial manifestation of wegner’s granulomatosis: diagnostic dilemma. Otology and Neurotology. 2011;32:966–1000. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

