Fear of COVID-19 as a precautionary measure to prevent the epidemic among the population of the Kurdistan Region/Iraq: based on a questionnaire survey
- PMID: 33968602
- PMCID: PMC8091631
- DOI: 10.1007/s10389-021-01568-0
Fear of COVID-19 as a precautionary measure to prevent the epidemic among the population of the Kurdistan Region/Iraq: based on a questionnaire survey
Abstract
Background and objectives: The World Health Organization (WHO) announced the appearance of a new coronavirus disease in Hubei province, China, to be a public health emergency of international concern. The objectives of this study can be highlighted through classifying the information sources for identifying protective practices, death probability, gender-death associations probability and education level.
Methodology: This is a descriptive design study conducted among the Kurdistan Region/Iraq population via an online application between 1 March and 1 May 2020. Three hundred twenty people participated in this questionnaire study. The data were collected through an online form, relying upon a self-report questionnaire. The questionnaire had three main parts. The first part is related to the socio-demographic characteristics of the sample, including gender, age, family status, address status and education level. The second part involves the items related to precautionary measures using none, sometimes, and always. The last part contains items related to death probability owing to other causes and this includes five categories: extremely low, low, intermediate, high and extremely high. The validity and reliability of this questionnaire were revised by the panel of experts before the data collection.
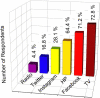
Results: The outcomes of the study revealed that the majority, ca. 73%, of the Kurdistan Region/Iraq population depended on TV to obtain information about COVID-19. Also, this investigation showed that there is a substantial association between participants with infection prevention and control practices relevant to COVID-19. Moreover, according to this study, there is a significant relationship between the death probability and COVID-19. Concurrently, there is not any significant association between other causes, namely cancer, heart diseases, diabetes and road traffic accidents, and the death probability.
Conclusion: This study showed that for the majority of the Kurdistan Region/Iraq population the most reliable source of information for any COVID-19 related updates is the TV broadcast. This study also indicated that there is strong association for the majority of individuals regarding their practices for prevention from COVID-19 and death probability with COVID-19. However, there is not any substantial association between the epidemic and the other deadly calamities and the death probability.
Keywords: COVID-19; Epidemic; Fear; Kurdistan region; Precautionary measure.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interestThe authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Phenomenon of depression and anxiety related to precautions for prevention among population during the outbreak of COVID-19 in Kurdistan Region of Iraq: based on questionnaire survey.Z Gesundh Wiss. 2022;30(3):567-571. doi: 10.1007/s10389-020-01325-9. Epub 2020 Jun 10. Z Gesundh Wiss. 2022. PMID: 32837841 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Covid-19 pandemic on surgical practice in Kurdistan, Iraq: An online cross-sectional survey.Int J Surg Open. 2020;27:47-51. doi: 10.1016/j.ijso.2020.10.014. Epub 2020 Nov 4. Int J Surg Open. 2020. PMID: 34568615 Free PMC article.
-
The Impact of Social Media on Panic During the COVID-19 Pandemic in Iraqi Kurdistan: Online Questionnaire Study.J Med Internet Res. 2020 May 19;22(5):e19556. doi: 10.2196/19556. J Med Internet Res. 2020. PMID: 32369026 Free PMC article.
-
Public sector reforms and their impact on the level of corruption: A systematic review.Campbell Syst Rev. 2021 May 24;17(2):e1173. doi: 10.1002/cl2.1173. eCollection 2021 Jun. Campbell Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 37131927 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Academic development for urologists in the Kurdistan region of Iraq.Arab J Urol. 2014 Mar;12(1):79-82. doi: 10.1016/j.aju.2013.08.003. Epub 2013 Sep 23. Arab J Urol. 2014. PMID: 26019930 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs) as a therapeutic agent of inflammatory disease and infectious COVID-19 virus: live or dead mesenchymal?Mol Biol Rep. 2024 Feb 10;51(1):295. doi: 10.1007/s11033-023-09174-x. Mol Biol Rep. 2024. PMID: 38340168 Review.
-
Exploring the interaction of quercetin-3-O-sophoroside with SARS-CoV-2 main proteins by theoretical studies: A probable prelude to control some variants of coronavirus including Delta.Arab J Chem. 2021 Oct;14(10):103353. doi: 10.1016/j.arabjc.2021.103353. Epub 2021 Jul 28. Arab J Chem. 2021. PMID: 34909059 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akram OK, Ismail S, Franco DJ. The significant of urban form of Erbil city, Iraq. Int J Eng Technol Manag Appl Sci. 2016;4:96–101.
-
- Al-Kubaisi QY, Gardi LM. Dust storm in Erbil city as a result of climatic change in Kurdistan Region Iraq. Iraqi J Sci. 2012;53:40–44.
-
- Cinelli M et al (2020) The COVID-19 social media infodemic. arXiv preprint. arXiv:2003.05004 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources