MALAT1 gene rs600231 polymorphism positively associated with acute coronary syndrome in Chinese population: a case-control study
- PMID: 33968621
- PMCID: PMC8102249
- DOI: 10.21037/cdt-20-906
MALAT1 gene rs600231 polymorphism positively associated with acute coronary syndrome in Chinese population: a case-control study
Abstract
Background: Metastasis-associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1 (MALAT1) has been recognized as a major player in the pathogenesis of coronary artery disease (CAD). The aim of the study was to determine the association between polymorphisms of the MALAT1 gene and acute coronary syndrome (ACS) in a Chinese population in Xinjiang.
Methods: In the case-control study, we genotyped three nucleotide polymorphisms (rs3200401, rs4102217, rs600231) of the MALAT1 gene using SNPscanTM typing assays (1,053 controls and 929 ACS patients). Furthermore, we explored a predictive model using MALAT1 rs600231 and clinical variables to predict the risk of ACS. Finally, the relative expression of long noncoding RNA (lncRNA) MALAT1 was also measured in 92 ACS patients and 92 controls using quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR).
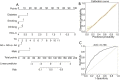
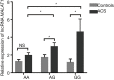
Results: The prevalence of the GG genotype of rs600231 in ACS group was higher than that in control group (15.7% vs. 14.7%, P=0.048). The dominant model differed (AG + GG vs. AA) and the G allele of rs600231 in ACS group was higher than that in control group (for dominant model: 66.2% vs. 60.9%, P=0.014; for allele: 41.0% vs. 37.8%, P=0.042). Multivariate logistic regression analysis and the predictive nomogram model showed that the dominant model of rs600231 remained an independent risk factor for ACS [odds ratio (OR) =1.32, 95% confidence interval (CI): 1.07-1.63, P=0.009]. The area under the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve (AUC) for the nomogram model for the prediction of ACS was 0.738 (95% CI: 0.716-0.761). In addition, in the AG and GG phenotypes, the relative expression of lncRNA MALAT1 was significantly higher in ACS patients than in controls with the same phenotypes (P<0.05). Among ACS group, compared to other genotype carriers, the relative expression level of MALAT1 in GG genotype carriers was higher (P<0.05).
Conclusions: The present study suggested that the AG and GG genotype of rs600231 in MALAT1 gene was independently associated with ACS, and could be a risk genetic marker of ACS in a Chinese population in Xinjiang.
Keywords: Metastasis-associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1 (MALAT1); acute coronary syndrome (ACS); polymorphism.
2021 Cardiovascular Diagnosis and Therapy. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at http://dx.doi.org/10.21037/cdt-20-906). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
LncRNA MALAT1 gene polymorphisms in coronary artery disease: a case-control study in a Chinese population.Biosci Rep. 2019 Mar 19;39(3):BSR20182213. doi: 10.1042/BSR20182213. Print 2019 Mar 29. Biosci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30833365 Free PMC article.
-
A genetic variant in the promoter of lncRNA MALAT1 is related to susceptibility of ischemic stroke.Lipids Health Dis. 2020 Apr 1;19(1):57. doi: 10.1186/s12944-020-01236-4. Lipids Health Dis. 2020. PMID: 32238151 Free PMC article.
-
Association of polymorphisms in MALAT1 with risk of coronary atherosclerotic heart disease in a Chinese population.Lipids Health Dis. 2018 Apr 10;17(1):75. doi: 10.1186/s12944-018-0728-2. Lipids Health Dis. 2018. PMID: 29631611 Free PMC article.
-
Association analyses of genetic variants in long non-coding RNA MALAT1 with breast cancer susceptibility and mRNA expression of MALAT1 in Chinese Han population.Gene. 2018 Feb 5;642:241-248. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2017.11.013. Epub 2017 Nov 13. Gene. 2018. PMID: 29146194
-
Association between peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-alpha, delta, and gamma polymorphisms and risk of coronary heart disease: A case-control study and meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2016 Aug;95(32):e4299. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000004299. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016. PMID: 27512842 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Potential Involvement of LncRNAs in Cardiometabolic Diseases.Genes (Basel). 2023 Jan 13;14(1):213. doi: 10.3390/genes14010213. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36672953 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long noncoding RNA MALAT1 polymorphism predicts MACCEs in patients with myocardial infarction.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2022 Apr 7;22(1):152. doi: 10.1186/s12872-022-02590-0. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2022. PMID: 35392816 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zhang H, Masoudi FA, Li J, et al. National assessment of early β-blocker therapy in patients with acute myocardial infarction in China, 2001-2011: The China Patient-centered Evaluative Assessment of Cardiac Events (PEACE)-Retrospective AMI Study. Am Heart J 2015;170:506-15.e1. 10.1016/j.ahj.2015.05.012 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hartman MHT, Eppinga RN, Vlaar PJJ, et al. The contemporary value of peak creatine kinase-MB after ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction above other clinical and angiographic characteristics in predicting infarct size, left ventricular ejection fraction, and mortality. Clin Cardiol 2017;40:322-8. 10.1002/clc.22663 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
