The Emerging World of Membrane Vesicles: Functional Relevance, Theranostic Avenues and Tools for Investigating Membrane Function
- PMID: 33968983
- PMCID: PMC8101706
- DOI: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.640355
The Emerging World of Membrane Vesicles: Functional Relevance, Theranostic Avenues and Tools for Investigating Membrane Function
Abstract
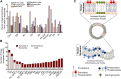
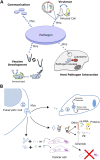
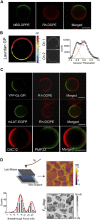
Lipids are essential components of cell membranes and govern various membrane functions. Lipid organization within membrane plane dictates recruitment of specific proteins and lipids into distinct nanoclusters that initiate cellular signaling while modulating protein and lipid functions. In addition, one of the most versatile function of lipids is the formation of diverse lipid membrane vesicles for regulating various cellular processes including intracellular trafficking of molecular cargo. In this review, we focus on the various kinds of membrane vesicles in eukaryotes and bacteria, their biogenesis, and their multifaceted functional roles in cellular communication, host-pathogen interactions and biotechnological applications. We elaborate on how their distinct lipid composition of membrane vesicles compared to parent cells enables early and non-invasive diagnosis of cancer and tuberculosis, while inspiring vaccine development and drug delivery platforms. Finally, we discuss the use of membrane vesicles as excellent tools for investigating membrane lateral organization and protein sorting, which is otherwise challenging but extremely crucial for normal cellular functioning. We present current limitations in this field and how the same could be addressed to propel a fundamental and technology-oriented future for extracellular membrane vesicles.
Keywords: diagnosis; drug delivery; exosomes; host-pathogen interactions; lipid biomarkers; lipids; membrane organization; membrane vesicles.
Copyright © 2021 Srivatsav and Kapoor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Abramowicz A., Wojakowska A., Marczak L., Lysek-Gladysinska M., Smolarz M., Story M. D., et al. (2019). Ionizing radiation affects the composition of the proteome of extracellular vesicles released by head-and-neck cancer cells in vitro . J. Radiat. Res. 60 (3), 289–297. 10.1093/jrr/rrz001 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Akuma P., Okagu O. D., Udenigwe C. C. (2019). Naturally occurring exosome vesicles as potential delivery vehicle for bioactive compounds. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 3. 10.3389/fsufs.2019.00023 - DOI
-
- Alaniz R. C., Deatherage B. L., Lara J. C., Cookson B. T. (2007). Membrane vesicles are immunogenic facsimiles of Salmonella typhimurium that potently activate dendritic cells, prime B and T cell responses, and stimulate protective immunity in vivo. J. Immunol. 179, 7692–7701. 10.4049/jimmunol.179.11.7692 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

