COMPARISON OF CONVENTIONAL HAND EXAMINATION ON SIX OPTIMISED DR SYSTEMS
- PMID: 33969425
- PMCID: PMC8808537
- DOI: 10.1093/rpd/ncab067
COMPARISON OF CONVENTIONAL HAND EXAMINATION ON SIX OPTIMISED DR SYSTEMS
Abstract
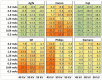
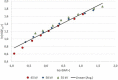
The purpose of this study was to investigate the challenges in comparing digital radiography (DR) systems from different vendors for various combinations of exposure factors in posterior-anterior hand radiographs. Image quality was evaluated for a range of tube voltages and tube current-time products using a technical contrast-detail (CDRAD) phantom and an anthropomorphic hand phantom. 900 technical CDRAD images were analysed providing quality figures of merit (IQFinv) and two experienced reporting radiographers using visual grading analysis (VGA) scored 108 anthropomorphic images. This study demonstrates the differences between the DR systems included. When compensating for variations in dose, Canon showed superior results for technical image quality and Fuji for visual image quality for a standard dose point at DR hand examination (ln(DAP) 1.1, 50 kV and 2.5 mAs).
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The influence of a novel edge enhancement software on image quality of DR hand images of patients with rheumatoid arthritis.Radiography (Lond). 2021 Aug;27(3):877-882. doi: 10.1016/j.radi.2021.02.006. Epub 2021 Mar 4. Radiography (Lond). 2021. PMID: 33676836
-
How does intelligent noise reduction software influence the image quality in pelvic digital radiography: A phantom study.J Med Imaging Radiat Sci. 2025 Mar;56(2):101814. doi: 10.1016/j.jmir.2024.101814. Epub 2024 Dec 6. J Med Imaging Radiat Sci. 2025. PMID: 39644735
-
CAN SCATTER CORRECTION SOFTWARE REPLACE A GRID IN DR PELVIC EXAMINATIONS?Radiat Prot Dosimetry. 2019 Dec 31;187(1):8-16. doi: 10.1093/rpd/ncz129. Radiat Prot Dosimetry. 2019. PMID: 31111927
-
New developed DR detector performs radiographs of hand, pelvic and premature chest anatomies at a lower radiation dose and/or a higher image quality.J Digit Imaging. 2014 Feb;27(1):68-76. doi: 10.1007/s10278-013-9635-2. J Digit Imaging. 2014. PMID: 24221693 Free PMC article.
-
Comparing the standard knee X-ray exposure factor, 10 kV rule, and modified 10 kV rule techniques in digital radiography to reduce patient radiation dose without loss of image quality.Radiography (Lond). 2024 Mar;30(2):574-581. doi: 10.1016/j.radi.2024.01.013. Epub 2024 Jan 31. Radiography (Lond). 2024. PMID: 38295494
Cited by
-
Typical and Local Diagnostic Reference Levels for Chest and Abdomen Radiography Examinations in Dubai Health Sector.J Imaging. 2025 Jan 13;11(1):21. doi: 10.3390/jimaging11010021. J Imaging. 2025. PMID: 39852334 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of body part thickness on low-contrast detail detection and radiation dose during adult chest radiography.J Med Radiat Sci. 2024 Mar;71(1):85-90. doi: 10.1002/jmrs.741. Epub 2023 Dec 4. J Med Radiat Sci. 2024. PMID: 38050453 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sundhedsstyrelsen, Statens Institut for Strålebeskyttelse . Udviklingen I brug af røntgenundersøgelser I Danmark (2015). http://sundhedsstyrelsen.dk/da/Feeds/∼/media/6BFF6AD1889B42AAAE71560759B... accessed 11 December 2020.
-
- Precht, H. et al. Does software optimization influence the radiologists' perception in low dose paediatric pelvic examinations? Radiography 25(2), 143–147 (2019). - PubMed
-
- Atci, I. B., Yilmaz, H., Antar, V., Ozdemir, N. G., Baran, O., Sadillioglu, S., Ozel, M., Turk, O., Yaman, M. and Topacoglu, H. What do we know about ALARA? Is our knowledge sufficient about radiation safety? J. Neurosurg. Sci. 61(6), 597–602 (2017). - PubMed
-
- ICRP . Managing patient dose in digital radiology. ICRP publication 93. Ann. ICRP 34, 1–73 (2004). - PubMed
-
- Båth, M. Evaluating imaging systems: practical applications. Radiat. Protect. Dosim 139(1e3), 26e36 (2010). - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

