Protective effect of aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 against rat corneal dysfunction caused by streptozotocin-induced type I diabetes
- PMID: 33969723
- PMCID: PMC8719039
- DOI: 10.1177/15353702211013308
Protective effect of aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 against rat corneal dysfunction caused by streptozotocin-induced type I diabetes
Abstract
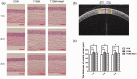
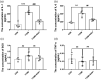
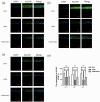
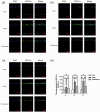
Aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 plays a pivotal role in detoxifying aldehydes, and our previous study revealed that aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 could alleviate diabetic retinopathy-associated damage. We aimed to characterize the potential role of aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 in diabetic keratopathy. Twenty-four rats with streptozotocin-induced (60 mg/kg, single intraperitoneal injection) type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) were divided the T1DM group and the T1DM + Alda1 (an activator of aldehyde dehydrogenase 2) group (5 mg/kg/d, intraperitoneal injection, 1/2/3 months), while an additional 12 healthy rats served as the control group. Corneal morphology was examined in vivo and in vitro at one, two, and three months after T1DM induction. Additionally, serum inflammatory factors were measured by ELISA, and the expression of corneal vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGF-A) and aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 was measured by immunofluorescence staining. Corneal cell death was evaluated by terminal-deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated nick end labeling (TUNEL) staining. Slit lamp analysis showed that the area of corneal epithelial cell injury in the T1DM + Alda1 group was significantly smaller than that in the T1DM group at one and two months after T1DM induction (all P < 0.05). OCT analysis and HE staining showed that the central corneal thickness (indication of corneal edema) and the epithelial keratinization level in the T1DM + Alda1 group was evidently decreased compared with those in the T1DM group (all P < 0.05). The serum inflammatory factors interleukin-1 and interleukin-6 were significantly upregulated in the T1DM group compared with the T1DM + Alda1 group at three months after T1DM induction (all P < 0.05), while there were no differences in SOD or TNF-α levels among all groups. Furthermore, corneal VEGF-A expression and corneal cell death in the T1DM + Alda1 group were dramatically reduced compared to those in the T1DM group (all P < 0.05). In conclusion, the aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 agonist Alda1 attenuated rat corneal dysfunction induced by T1DM by alleviating corneal edema, decreasing corneal cell death, and downregulating corneal VEGF-A expression.
Keywords: Aldehyde dehydrogenase 2; VEGF-A; cornea; diabetes mellitus; diabetic keratopathy; inflammation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Saeedi P, Petersohn I, Salpea P, Malanda B, Karuranga S, Unwin N, Colagiuri S, Guariguata L, Motala AA, Ogurtsova K, Shaw JE, Bright D, Williams R. Global and regional diabetes prevalence estimates for 2019 and projections for 2030 and 2045: results from the international diabetes federation diabetes atlas, 9(th) edition. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2019; 157:107843. - PubMed
-
- Abdelkader H, Patel DV, McGhee C, Alany RG. New therapeutic approaches in the treatment of diabetic keratopathy: a review. Clin Exp Ophthalmol 2011; 39:259–70 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

