Risk factors associated with health-related quality of life in pediatric asthma
- PMID: 33970048
- PMCID: PMC10358580
- DOI: 10.1177/00368504211013657
Risk factors associated with health-related quality of life in pediatric asthma
Abstract
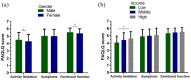
To evaluate the quality of life (QOL) of children with asthma and analyze the related factors. A total of 360 children diagnosed with asthma were enrolled. We conducted the pediatric asthma quality of life questionnaire (PAQLQ). The differences in clinical characteristics between the two groups were compared. Clinical characteristics were compared between high and low QOL. More female was observed in low QOL group (p = 0.013). Patients with higher income (p = 0.003) were shown with higher QOL. Female patients presented significantly lower values for activity limitation (p = 0.016) and emotional function (p = 0.016) as compared to male patients. For patients who have low income, the QOL scores for dimensions of activity limitation was significantly worse than those have higher income (p = 0.001). Univariable results showed that gender (p = 0.013) and income (p = 0.001) were factors associated with QOL in asthma children. However, multivariate analysis suggested that only gender (OR = 0.558, p = 0.008) and income (OR = 1.762, p < 0.001) were the independent factors that affected the QOL levels. In this study, we found that the QOL dimensions of pediatric asthma differed between various subpopulations. For patients with risk factors of poor QOL, target intervention is advised in order to increase QOL.
Keywords: Asthma; pediatric; quality of life; risk factors.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
References
-
- 2020 GINA Report, Global Strategy for Asthma Management and Prevention. From the global strategy for asthma management and prevention, Global Initiative for Asthma (GINA), https://ginasthma.org/gina-reports/
-
- Josie KL, Greenley RN, Drotar D. Health-related quality-of-life measures for children with asthma: reliability and validity of the Children’s Health Survey for Asthma and the Pediatric Quality of Life Inventory 3.0 Asthma Module. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 2007; 98(3): 218–224. - PubMed
-
- Monteiro FP, Sole D, Wandalsen G. Quality of life of asthmatic children and adolescents: Portuguese translation, adaptation, and validation of the questionnaire “Pediatric Quality of Life (PedsQL) Asthma Module”. J Asthma 2017; 54(9): 983–989. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

