Chromatin structure-dependent histone incorporation revealed by a genome-wide deposition assay
- PMID: 33970102
- PMCID: PMC8110306
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.66290
Chromatin structure-dependent histone incorporation revealed by a genome-wide deposition assay
Abstract
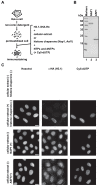
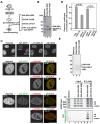
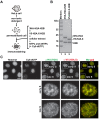
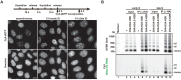
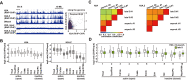
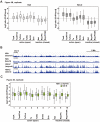
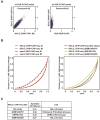
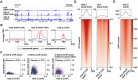
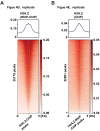
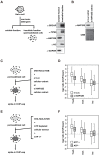
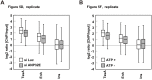
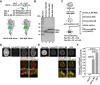
In eukaryotes, histone variant distribution within the genome is the key epigenetic feature. To understand how each histone variant is targeted to the genome, we developed a new method, the RhIP (Reconstituted histone complex Incorporation into chromatin of Permeabilized cell) assay, in which epitope-tagged histone complexes are introduced into permeabilized cells and incorporated into their chromatin. Using this method, we found that H3.1 and H3.3 were incorporated into chromatin in replication-dependent and -independent manners, respectively. We further found that the incorporation of histones H2A and H2A.Z mainly occurred at less condensed chromatin (open), suggesting that condensed chromatin (closed) is a barrier for histone incorporation. To overcome this barrier, H2A, but not H2A.Z, uses a replication-coupled deposition mechanism. Our study revealed that the combination of chromatin structure and DNA replication dictates the differential histone deposition to maintain the epigenetic chromatin states.
Keywords: H2A.Z; Histone; chromatin; chromosomes; gene expression; human; nucleosome.
© 2021, Tachiwana et al.
Conflict of interest statement
HT, MD, KM, AH, YS, RK, YO, HK, HK, NS No competing interests declared
Figures
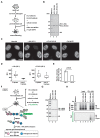
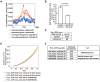
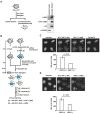
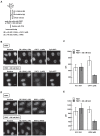
References
-
- Altaf M, Auger A, Monnet-Saksouk J, Brodeur J, Piquet S, Cramet M, Bouchard N, Lacoste N, Utley RT, Gaudreau L, Côté J. NuA4-dependent acetylation of nucleosomal histones H4 and H2A directly stimulates incorporation of H2A.Z by the SWR1 complex. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2010;285:15966–15977. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.117069. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

