Uncovering a novel role of PLCβ4 in selectively mediating TCR signaling in CD8+ but not CD4+ T cells
- PMID: 33970189
- PMCID: PMC8111461
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20201763
Uncovering a novel role of PLCβ4 in selectively mediating TCR signaling in CD8+ but not CD4+ T cells
Abstract
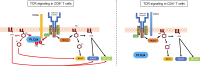
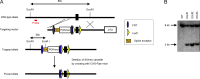
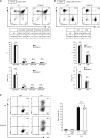
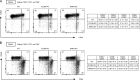
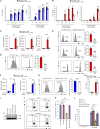
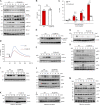
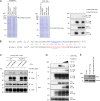
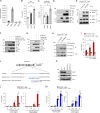
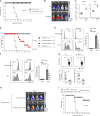
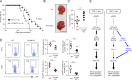
Because of their common signaling molecules, the main T cell receptor (TCR) signaling cascades in CD4+ and CD8+ T cells are considered qualitatively identical. Herein, we show that TCR signaling in CD8+ T cells is qualitatively different from that in CD4+ T cells, since CD8α ignites another cardinal signaling cascade involving phospholipase C β4 (PLCβ4). TCR-mediated responses were severely impaired in PLCβ4-deficient CD8+ T cells, whereas those in CD4+ T cells were intact. PLCβ4-deficient CD8+ T cells showed perturbed activation of peripheral TCR signaling pathways downstream of IP3 generation. Binding of PLCβ4 to the cytoplasmic tail of CD8α was important for CD8+ T cell activation. Furthermore, GNAQ interacted with PLCβ4, mediated double phosphorylation on threonine 886 and serine 890 positions of PLCβ4, and activated CD8+ T cells in a PLCβ4-dependent fashion. PLCβ4-deficient mice exhibited defective antiparasitic host defense and antitumor immune responses. Altogether, PLCβ4 differentiates TCR signaling in CD4+ and CD8+ T cells and selectively promotes CD8+ T cell-dependent adaptive immunity.
© 2021 Sasai et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures: H. Nagaoka reported personal fees from Ehime University outside the submitted work. E. Takashima reported personal fees from Ehime University outside the submitted work. No other disclosures were reported.
Figures





References
-
- Anderson, D.L., and Tsoukas C.D.. 1989. Cholera toxin inhibits resting human T cell activation via a cAMP-independent pathway. J. Immunol. 143:3647–3652. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

