Staphylococcus aureus ST228 and ST239 as models for expression studies of diverse markers during osteoblast infection and persistence
- PMID: 33970534
- PMCID: PMC8087985
- DOI: 10.1002/mbo3.1178
Staphylococcus aureus ST228 and ST239 as models for expression studies of diverse markers during osteoblast infection and persistence
Abstract
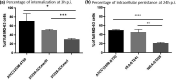
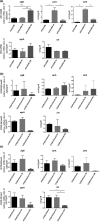
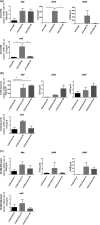
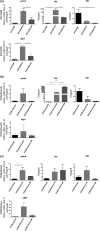
The ability of S. aureus to infect bone and osteoblasts is correlated with its incredible virulence armamentarium that can mediate the invasion/internalization process, cytotoxicity, membrane damage, and intracellular persistence. We comparatively analyzed the interaction, persistence, and modulation of expression of selected genes and cell viability in an ex vivo model using human MG-63 osteoblasts of two previously studied and well-characterized S. aureus clinical strains belonging to the ST239-SCCmecIII-t037 and ST228-SCCmecI-t041 clones at 3 h and 24 h post-infection (p.i). S. aureus ATCC12598 ST30-t076 was used as a control strain. Using imaging flow cytometry (IFC), we found that these strains invaded and persisted in MG-63 osteoblasts to different extents. The invasion was evaluated at 3 h p.i and persistence at 24 h p.i., in particular: ATCC12598 internalized in 70% and persisted in 50% of MG-63 cells; ST239-SCCmecIII internalized in 50% and persisted in 45% of MG-63 cells; and ST228-SCCmecI internalized in 30% and persisted in 20% of MG-63 cells. During the infection period, ST239-III exerted significant cytotoxic activity resulting from overexpression of hla and psmA and increased expression of the genes involved in adhesion, probably due to the release and re-entry of bacteria inside MG-63 cells at 24 h p.i. The lower invasiveness of ST228-I was also associated with non-cytotoxic activity inside osteoblasts. This clone was unable to activate sufficient cellular reaction and succumbed inside MG-63 cells. Our findings support the idea of considering new strategies, based on a translational approach-eukaryotic host-pathogen interaction (EHPI)-and to be applied on a large scale, to predict S. aureus /osteoblast interaction and treat bone infections. Such strategies rely on the study of the genetic and biochemical basis of both pathogen and host.
Keywords: MRSA; ST228; ST239; crosstalk mechanism; osteoblast; virulence toxin.
© 2021 The Authors. MicrobiologyOpen published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures
References
-
- Bongiorno, D., Mongelli, G., Stefani, S., & Campanile, F. (2018). Burden of rifampicin‐ and methicillin‐resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Italy. Microbial Drug Resistance, 24, 732–738. - PubMed
-
- Botelho, A. M., Cerqueira e Costa, M. O., Moustafa, A. M., Beltrame, C. O., Ferreira, F. A., Côrtes, M. F., Costa, B. S., Silva, D. N., Bandeira, P. T., Lima, N. C., & Souza, R. C. (2019). Local diversification of methicillin‐resistant Staphylococcus aureus ST239 in South America after its rapid worldwide dissemination. Frontiers in Microbiology, 10, 82. 10.3389/fmicb.2019.00082. eCollection. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cafiso, V., Bertuccio, T., Purrello, S., Campanile, F., Mammina, C., Sartor, A., Raglio, A., & Stefani, S. (2014). dltA overexpression: A strain‐independent keystone of daptomycin resistance in methicillin‐resistant Staphylococcus aureus . International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents, 43(1), 26–31. 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2013.10.001 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cafiso, V., Bertuccio, T., Spina, D., Purrello, S., Blandino, G., & Stefani, S. (2012). A novel δ‐hemolysis screening method for detecting heteroresistant vancomycin‐intermediate Staphylococcus aureus and vancomycin‐intermediate S. aureus . Journal of Clinical Microbiology, 50(5), 1742–1744. 10.1128/JCM.06307-11 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

