Overexpression of wild-type IL-7Rα promotes T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma
- PMID: 33970999
- PMCID: PMC8462360
- DOI: 10.1182/blood.2019000553
Overexpression of wild-type IL-7Rα promotes T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma
Erratum in
-
Silva A, Almeida ARM, Cachucho A, et al. Overexpression of wild-type IL-7Rα promotes T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma. Blood. 2021;138(12):1040-1052.Blood. 2024 May 16;143(20):2108-2110. doi: 10.1182/blood.2024024693. Blood. 2024. PMID: 38753359 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Tight regulation of IL-7Rα expression is essential for normal T-cell development. IL-7Rα gain-of-function mutations are known drivers of T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL). Although a subset of patients with T-ALL display high IL7R messenger RNA levels and cases with IL7R gains have been reported, the impact of IL-7Rα overexpression, rather than mutational activation, during leukemogenesis remains unclear. In this study, overexpressed IL-7Rα in tetracycline-inducible Il7r transgenic and Rosa26 IL7R knockin mice drove potential thymocyte self-renewal, and thymus hyperplasia related to increased proliferation of T-cell precursors, which subsequently infiltrated lymph nodes, spleen, and bone marrow, ultimately leading to fatal leukemia. The tumors mimicked key features of human T-ALL, including heterogeneity in immunophenotype and genetic subtype between cases, frequent hyperactivation of the PI3K/Akt pathway paralleled by downregulation of p27Kip1 and upregulation of Bcl-2, and gene expression signatures evidencing activation of JAK/STAT, PI3K/Akt/mTOR and Notch signaling. Notably, we also found that established tumors may no longer require high levels of IL-7R expression upon secondary transplantation and progressed in the absence of IL-7, but remain sensitive to inhibitors of IL-7R-mediated signaling ruxolitinib (Jak1), AZD1208 (Pim), dactolisib (PI3K/mTOR), palbociclib (Cdk4/6), and venetoclax (Bcl-2). The relevance of these findings for human disease are highlighted by the fact that samples from patients with T-ALL with high wild-type IL7R expression display a transcriptional signature resembling that of IL-7-stimulated pro-T cells and, critically, of IL7R-mutant cases of T-ALL. Overall, our study demonstrates that high expression of IL-7Rα can promote T-cell tumorigenesis, even in the absence of IL-7Rα mutational activation.
© 2021 by The American Society of Hematology.
Figures


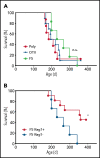




Comment in
-
T-ALL and the talented Mr IL7Rα.Blood. 2021 Sep 23;138(12):1003-1004. doi: 10.1182/blood.2021012184. Blood. 2021. PMID: 34554220 No abstract available.
References
-
- Fry TJ, Mackall CL.. Interleukin-7: from bench to clinic. Blood. 2002;99(11):3892-3904. - PubMed
-
- Barata JT, Durum SK, Seddon B.. Flip the coin: IL-7 and IL-7R in health and disease. Nat Immunol. 2019;20(12):1584-1593. - PubMed
-
- Puel A, Ziegler SF, Buckley RH, Leonard WJ.. Defective IL7R expression in T(-)B(+)NK(+) severe combined immunodeficiency. Nat Genet. 1998;20(4):394-397. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

