Sensitive on-site detection of SARS-CoV-2 by ID NOW COVID-19
- PMID: 33971264
- PMCID: PMC8105142
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mcp.2021.101742
Sensitive on-site detection of SARS-CoV-2 by ID NOW COVID-19
Abstract
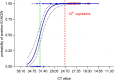
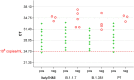
Point of care detection of SARS-CoV-2 is one pillar in a containment strategy and important to break infection chains. Here we report the sensitive, specific and robust detection of SARS-CoV-2 and respective variants of concern by the ID NOW COVID-19 device.
Keywords: COVID-19; Diagnostics; On-site detection; SARS CoV-2.
Copyright © 2021 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- WHO/WHE/2021.02, COVID-19 Strategic Preparedness and Response Plan. SPRP 2021; 2021.
-
- Chu D.K.W., Pan Y., Cheng S.M.S., Hui K.P.Y., Krishnan P., Liu Y., Ng D.Y.M., Wan C.K.C., Yang P., Wang Q., Peiris M., Poon L.L.M. Molecular diagnosis of a novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) causing an outbreak of pneumonia. Clin. Chem. 2020;66:549–555. doi: 10.1093/clinchem/hvaa029. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Corman V.M., Landt O., Kaiser M., Molenkamp R., Meijer A., Chu D.K.W., Bleicker T., Brünink S., Schneider J., Schmidt M.L., Mulders D.G.J.C., Haagmans B.L., Van Der Veer B., Van Den Brink S., Wijsman L., Goderski G., Romette J.L., Ellis J., Zambon M., Peiris M., Goossens H., Reusken C., Koopmans M.P.G., Drosten C. Detection of 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) by real-time RT-PCR. Euro Surveill. 2020;25 doi: 10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2020.25.3.2000045. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

