Classification of COVID-19 chest X-Ray and CT images using a type of dynamic CNN modification method
- PMID: 33971427
- PMCID: PMC8081579
- DOI: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2021.104425
Classification of COVID-19 chest X-Ray and CT images using a type of dynamic CNN modification method
Abstract
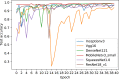
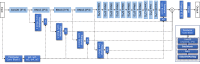
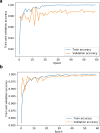
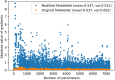
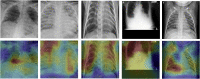
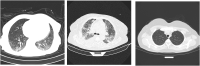
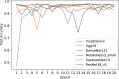
Understanding and classifying Chest X-Ray (CXR) and computerised tomography (CT) images are of great significance for COVID-19 diagnosis. The existing research on the classification for COVID-19 cases faces the challenges of data imbalance, insufficient generalisability, the lack of comparative study, etc. To address these problems, this paper proposes a type of modified MobileNet to classify COVID-19 CXR images and a modified ResNet architecture for CT image classification. In particular, a modification method of convolutional neural networks (CNN) is designed to solve the gradient vanishing problem and improve the classification performance through dynamically combining features in different layers of a CNN. The modified MobileNet is applied to the classification of COVID-19, Tuberculosis, viral pneumonia (with the exception of COVID-19), bacterial pneumonia and normal controls using CXR images. Also, the proposed modified ResNet is used for the classification of COVID-19, non-COVID-19 infections and normal controls using CT images. The results show that the proposed methods achieve 99.6% test accuracy on the five-category CXR image dataset and 99.3% test accuracy on the CT image dataset. Six advanced CNN architectures and two specific COVID-19 detection models, i.e., COVID-Net and COVIDNet-CT are used in comparative studies. Two benchmark datasets and a CXR image dataset which combines eight different CXR image sources are employed to evaluate the performance of the above models. The results show that the proposed methods outperform the comparative models in classification accuracy, sensitivity, and precision, which demonstrate their potential in computer-aided diagnosis for healthcare applications.
Keywords: COVID-19 detection; Chest X-Ray and CT images; Deep learning; Modified CNN.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

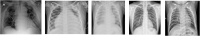
- •
COVID-19 CXR images are from the open source GitHub repository ieee8023/covid-chestxray-dataset (DS 1) [36], Actualmed-COVID-chestxray-dataset (DS 2), Fig. 1-COVID-chestx-ray-dataset (DS 3) [37], COVID-19 Radiography Database (DS 4) [24]. Data preparing for COVID-19 images in this paper referred to the code provided in the GitHub repository COVIDx Dataset contributed by Linda Wang et al. [11].
- •
The images of tuberculosis positive cases are from the dataset [38] which include CXR databases respectively obtained in Shenzhen, China and Montgomery, USA (DS 5), and the data source TB Portals Program, Office of Cyber Infrastructure and Computational Biology (OCICB), National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID) (DS 6).
- •
The bacterial and viral pneumonia CXR images are from Pneumonia Classification Dataset (DS 7) [39].
- •
The CXR images of normal controls are from COVID-19 Radiography Database (DS 4) [24].
Similar articles
-
Deep Learning Algorithm for COVID-19 Classification Using Chest X-Ray Images.Comput Math Methods Med. 2021 Nov 9;2021:9269173. doi: 10.1155/2021/9269173. eCollection 2021. Comput Math Methods Med. 2021. PMID: 34795794 Free PMC article.
-
Chest X-ray image phase features for improved diagnosis of COVID-19 using convolutional neural network.Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg. 2021 Feb;16(2):197-206. doi: 10.1007/s11548-020-02305-w. Epub 2021 Jan 9. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg. 2021. PMID: 33420641 Free PMC article.
-
COVID-DSNet: A novel deep convolutional neural network for detection of coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) cases from CT and Chest X-Ray images.Artif Intell Med. 2022 Dec;134:102427. doi: 10.1016/j.artmed.2022.102427. Epub 2022 Oct 17. Artif Intell Med. 2022. PMID: 36462906 Free PMC article.
-
COVID-19 image classification using deep learning: Advances, challenges and opportunities.Comput Biol Med. 2022 May;144:105350. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2022.105350. Epub 2022 Mar 3. Comput Biol Med. 2022. PMID: 35305501 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development and integration of VGG and dense transfer-learning systems supported with diverse lung images for discovery of the Coronavirus identity.Inform Med Unlocked. 2022;32:101004. doi: 10.1016/j.imu.2022.101004. Epub 2022 Jul 8. Inform Med Unlocked. 2022. PMID: 35822170 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Review of COVID-19 testing and diagnostic methods.Talanta. 2022 Jul 1;244:123409. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2022.123409. Epub 2022 Mar 31. Talanta. 2022. PMID: 35390680 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An Analysis of New Feature Extraction Methods Based on Machine Learning Methods for Classification Radiological Images.Comput Intell Neurosci. 2022 May 25;2022:3035426. doi: 10.1155/2022/3035426. eCollection 2022. Comput Intell Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35634075 Free PMC article.
-
Deep learning using nasal endoscopy and T2-weighted MRI for prediction of sinonasal inverted papilloma-associated squamous cell carcinoma: an exploratory study.Eur Radiol Exp. 2025 Jul 21;9(1):68. doi: 10.1186/s41747-025-00610-0. Eur Radiol Exp. 2025. PMID: 40691342 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in artificial intelligence in thyroid-associated ophthalmopathy.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Apr 23;15:1356055. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1356055. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 38715793 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Learning-to-augment incorporated noise-robust deep CNN for detection of COVID-19 in noisy X-ray images.J Comput Sci. 2022 Sep;63:101763. doi: 10.1016/j.jocs.2022.101763. Epub 2022 Jul 7. J Comput Sci. 2022. PMID: 35818367 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Verma D., Bose C., Tufchi N., Pant K., Tripathi V., Thapliyal A. An efficient framework for identification of tuberculosis and pneumonia in chest x-ray images using neural network. Procedia Computer Science. 2020;171:217–224.
-
- J. Zhang, Y. Xie, Y. Li, C. Shen, Y. Xia, Covid-19 Screening on Chest X-Ray Images Using Deep Learning Based Anomaly Detection, arXiv preprint arXiv:2003.12338.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

