Sepsis and Mortality Prediction in Very Low Birth Weight Infants: Analysis of HeRO and nSOFA
- PMID: 33971672
- PMCID: PMC8578589
- DOI: 10.1055/s-0041-1728829
Sepsis and Mortality Prediction in Very Low Birth Weight Infants: Analysis of HeRO and nSOFA
Abstract
Objective: Scores to predict sepsis or define sepsis severity could improve care for very low birth weight (VLBW) infants. The heart rate characteristics (HRC) index (HeRO score) was developed as an early warning system for late-onset sepsis (LOS), and also rises before necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC). The neonatal sequential organ failure assessment (nSOFA) was developed to predict sepsis-associated mortality using respiratory, hemodynamic, and hematologic data. The aim of this study was to analyze the HRC index and nSOFA near blood cultures in VLBW infants relative to diagnosis and sepsis-associated mortality.
Study design: Retrospective, single-center study of VLBW infants from 2011 to 2019. We analyzed HRC index and nSOFA around blood cultures diagnosed as LOS/NEC. In a subgroup of the cohort, we analyzed HRC and nSOFA near the first sepsis-like illness (SLI) or sepsis ruled-out (SRO) compared with LOS/NEC. We compared scores by diagnosis and mortality during treatment.
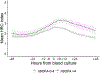
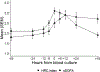
Results: We analyzed 179 LOS/NEC, 93 SLI, and 96 SRO blood culture events. In LOS/NEC, the HRC index increased before the blood culture, while nSOFA increased at the time of culture. Both scores were higher in nonsurvivors compared with survivors and in LOS/NEC compared with SRO. The nSOFA 12 hours after the time of blood culture predicted mortality during treatment better than any other time point analyzed (area under the curve 0.91).
Conclusion: The HRC index provides earlier warning of imminent sepsis, whereas nSOFA after blood culture provides better prediction of mortality.
Key points: · The HRC index and nSOFA provide complementary information on sepsis risk and sepsis-related mortality risk.. · This study adds to existing literature evaluating these risk scores independently by analyzing them together and in cases of not only proven but also suspected infections.. · The impact of combining risk models could be improved outcomes for premature infants..
Thieme. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
J.L.W. has served as a paid consultant for Evolve Biosystems. The other authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
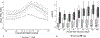
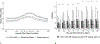
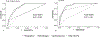
References
-
- Stoll BJ, Hansen NI, Adams-Chapman I, et al.; National Institute of Child Health and Human Development Neonatal Research Network. Neurodevelopmental and growth impairment among extremely low-birth-weight infants with neonatal infection. JAMA 2004;292(19):2357–2365 - PubMed
-
- Griffin MP, Moorman JR. Toward the early diagnosis of neonatal sepsis and sepsis-like illness using novel heart rate analysis. Pediatrics 2001;107(01):97–104 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

