Increasing prevalence of fasting hyperglycemia in adolescents aged 10-18 years and its relationship with metabolic indicators: the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Study (KNHANES), 2007-2018
- PMID: 33971707
- PMCID: PMC8984745
- DOI: 10.6065/apem.2142068.034
Increasing prevalence of fasting hyperglycemia in adolescents aged 10-18 years and its relationship with metabolic indicators: the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Study (KNHANES), 2007-2018
Abstract
Purpose: Pediatric diabetes is a common health burden worldwide. This study aimed to investigate the prevalence of fasting hyperglycemia in Korean youth aged 10-18 years and to evaluate its association with metabolic indicators.
Methods: To assess the risk of diabetes in domestic children and adolescents, the prevalence of fasting hyperglycemia was calculated, a trend was evaluated using multi-year Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES) data, and multivariate analysis was performed to evaluate the relationships between hyperglycemia and metabolic factors.
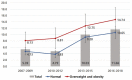
Results: The prevalence of fasting hyperglycemia, defined as impaired fasting glucose (fasting glucose level > 100 mg/dL and < 125 mg/dL), or diabetes mellitus (fasting glucose ≥ 126 mg/dL) was estimated in Korean teenagers. The prevalence increased from the fourth (2007-2009) to the fifth (2010-2012), sixth (2013-2015), and seventh (2016-2018) KNHANES surveys, from 5.39 to 4.79, 10.03, and 11.66 per 100 persons, respectively. In multivariate analysis, systolic blood pressure and serum triglycerides were higher in the fasting hyperglycemia group; systolic blood pressures were 109.83 mmHg and 112.64 mmHg and serum triglycerides were 81.59 mg/dL and 89.60 mg/dL in the normal blood glucose and fasting hyperglycemia groups, respectively.
Conclusion: The prevalence of fasting hyperglycemia among children and adolescents has increased over the past decade, and this increase is potentially associated with metabolic abnormalities such as hypertension and hypertriglyceridemia. Effort is urgently required to reduce this chronic medical burden in adolescence.
Keywords: Adolescents; Child; Diabetes; Hyperglycemia; Metabolic indicators.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
References
-
- Codoner-Franch P, Valls-Belles V, Arilla-Codoner A, Alonso-Iglesias E. Oxidant mechanisms in childhood obesity: the link between inflammation and oxidative stress. Transl Res. 2011;158:369–84. - PubMed
-
- Polonsky KS, Sturis J, Bell GI. Non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus - a genetically programmed failure of the beta cell to compensate for insulin resistance. N Engl J Med. 1996;334:777–83. - PubMed
-
- Wang CC, Goalstone ML, Draznin B. Molecular mechanisms of insulin resistance that impact cardiovascular biology. Diabetes. 2004;53:2735–40. - PubMed
-
- Seidell JC, Halberstadt J. The global burden of obesity and the challenges of prevention. Ann Nutr Metab. 2015;66:7–12. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

