The furosemide stress test: current use and future potential
- PMID: 33971784
- PMCID: PMC8118439
- DOI: 10.1080/0886022X.2021.1906701
The furosemide stress test: current use and future potential
Abstract
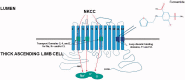
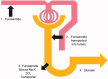
Loop diuretics are among the most widely used drugs worldwide and are commonly employed in the management of complications associated with acute kidney injury (AKI), namely volume overload and electrolyte management. The use of loop diuretics in critically ill patients with AKI is paramount to preventing or treating pulmonary edema. The naturetic response to a loop diuretic is based on its unique renal pharmacology. Our review article summarizes the pharmacology of furosemide in the intact nephron and discusses how this response might be altered by the presence of AKI. We discuss the increasing body of literature on the latest clinical utility of furosemide namely, it's challenge test, known as the furosemide stress test which has highlighted a new and novel role for furosemide over the past number of years. This test assists with the identification of AKI subjects at higher risk of AKI progression and the need for renal replacement therapy. The stress test can also predict cessation of continuous renal replacement therapy in patients with established AKI. On the basis of the evidence presented in this review, we propose future potential studies of furosemide in AKI.
Keywords: Furosemide; acute kidney injury; renal replacement therapy; risk assessment; stress test.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures
References
-
- Hobson CE, Yavas S, Segal MS, et al. Acute kidney injury is associated with increased long-term mortality after cardiothoracic surgery. Circulation. 2009;119(18):2444–2453. - PubMed
-
- Singbartl K, Kellum JA.. AKI in the ICU: definition, epidemiology, risk stratification, and outcomes. Kidney Int. 2012;81(9):819–825. - PubMed
-
- Amdur RL, Chawla LS, Amodeo S, et al. Outcomes following diagnosis of acute renal failure in U.S. veterans: focus on acute tubular necrosis. Kidney Int. 2009;76(10):1089–1097. - PubMed
-
- McMahon BA, Koyner JL.. Risk stratification for acute kidney injury: are biomarkers enough? Adv Chronic Kidney Dis. 2016;23(3):167–178. - PubMed
-
- Brater DC. Diuretic therapy. N Engl J Med. 1998;339(6):387–395. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
