A novel risk-predicted nomogram for sepsis associated-acute kidney injury among critically ill patients
- PMID: 33971853
- PMCID: PMC8111773
- DOI: 10.1186/s12882-021-02379-x
A novel risk-predicted nomogram for sepsis associated-acute kidney injury among critically ill patients
Abstract
Background: Acute kidney injury (AKI) is a prevalent and severe complication of sepsis contributing to high morbidity and mortality among critically ill patients. In this retrospective study, we develop a novel risk-predicted nomogram of sepsis associated-AKI (SA-AKI).
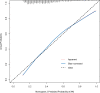
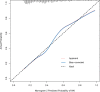
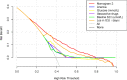
Methods: A total of 2,871 patients from the Medical Information Mart for Intensive Care III (MIMIC-III) critical care database were randomly assigned to primary (2,012 patients) and validation (859 patients) cohorts. A risk-predicted nomogram for SA-AKI was developed through multivariate logistic regression analysis in the primary cohort while the nomogram was evaluated in the validation cohort. Nomogram discrimination and calibration were assessed using C-index and calibration curves in the primary and external validation cohorts. The clinical utility of the final nomogram was evaluated using decision curve analysis.
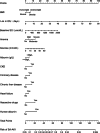
Results: Risk predictors included in the prediction nomogram included length of stay in intensive care unit (LOS in ICU), baseline serum creatinine (SCr), glucose, anemia, and vasoactive drugs. Nomogram revealed moderate discrimination and calibration in estimating the risk of SA-AKI, with an unadjusted C-index of 0.752, 95 %Cl (0.730-0.774), and a bootstrap-corrected C index of 0.749. Application of the nomogram in the validation cohort provided moderate discrimination (C-index, 0.757 [95 % CI, 0.724-0.790]) and good calibration. Besides, the decision curve analysis (DCA) confirmed the clinical usefulness of the nomogram.
Conclusions: This study developed and validated an AKI risk prediction nomogram applied to critically ill patients with sepsis, which may help identify reasonable risk judgments and treatment strategies to a certain extent. Nevertheless, further verification using external data is essential to enhance its applicability in clinical practice.
Keywords: Acute kidney injury; Intensive care unit; Nomogram; Prediction; Sepsis.
Conflict of interest statement
None of the authors have any conflicts of interests to declare.
Figures

References
-
- Rhodes A, Evans LE, Alhazzani W, Levy MM, Antonelli M, Ferrer R, Kumar A, Sevransky JE, Sprung CL, Nunnally ME, et al. Surviving Sepsis Campaign: International Guidelines for Management of Sepsis and Septic Shock: 2016. Intensive care medicine. 2017;43(3):304–377. - PubMed
-
- Skube SJ, Katz SA, Chipman JG, Tignanelli CJ. Acute Kidney Injury and Sepsis. Surgical infections. 2018;19(2):216–224. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

