IL-9-triggered lncRNA Gm13568 regulates Notch1 in astrocytes through interaction with CBP/P300: contribute to the pathogenesis of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis
- PMID: 33971906
- PMCID: PMC8112022
- DOI: 10.1186/s12974-021-02156-5
IL-9-triggered lncRNA Gm13568 regulates Notch1 in astrocytes through interaction with CBP/P300: contribute to the pathogenesis of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis
Abstract
Background: Interleukin 9 (IL-9), produced mainly by T helper 9 (Th9) cells, has been recognized as an important regulator in multiple sclerosis (MS) and its animal model, experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE). Astrocytes respond to IL-9 and reactive astrocytes always associate with blood-brain barrier damage, immune cell infiltration, and spinal injury in MS and EAE. Several long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) with aberrant expression have been identified in the pathogenesis of MS. Here, we examined the effects of lncRNA Gm13568 (a co-upregulated lncRNA both in EAE mice and in mouse primary astrocytes activated by IL-9) on the activation of astrocytes and the process of EAE.
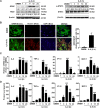
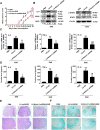
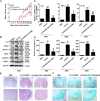
Methods: In vitro, shRNA-recombinant lentivirus with glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) promoter were performed to determine the relative gene expression and proinflammatory cytokines production in IL-9 treated-astrocytes using Western blot, real-time PCR, and Cytometric Bead Array, respectively. RIP and ChIP assays were analyzed for the mechanism of lncRNA Gm13568 regulating gene expression. Immunofluorescence assays was performed to measure the protein expression in astrocytes. In vivo, H&E staining and LFB staining were applied to detect the inflammatory cells infiltrations and the medullary sheath damage in spinal cords of EAE mice infected by the recombinant lentivirus. Results were analyzed by one-way ANOVA or Student's t test, as appropriate.
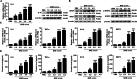
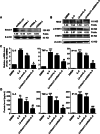
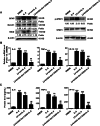
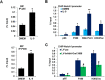
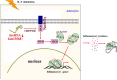
Results: Knockdown of the endogenous lncRNA Gm13568 remarkably inhibits the Notch1 expression, astrocytosis, and the phosphorylation of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (p-STAT3) as well as the production of inflammatory cytokines and chemokines (IL-6, TNF-α, IP-10) in IL-9-activated astrocytes, in which Gm13568 associates with the transcriptional co-activators CBP/P300 which are enriched in the promoter of Notch1 genes. More importantly, inhibiting Gm13568 with lentiviral vector in astrocytes ameliorates significantly inflammation and demyelination in EAE mice, therefore delaying the EAE process.
Conclusions: These findings uncover that Gm13568 regulates the production of inflammatory cytokines in active astrocytes and affects the pathogenesis of EAE through the Notch1/STAT3 pathway. LncRNA Gm13568 may be a promising target for treating MS and demyelinating diseases.
Keywords: Astrocytes; Experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE); IL-9; Inflammatory cytokines; LncRNA Gm13568; Notch1.
Conflict of interest statement
None of the authors have any conflicts of interest in this study.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 81971179/the National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82071304, 81671149/the National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81702027/the National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81461138036/the National Natural Science Foundation of China
- BK20191463/the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

