DPSCs treated by TGF-β1 regulate angiogenic sprouting of three-dimensionally co-cultured HUVECs and DPSCs through VEGF-Ang-Tie2 signaling
- PMID: 33971955
- PMCID: PMC8112067
- DOI: 10.1186/s13287-021-02349-y
DPSCs treated by TGF-β1 regulate angiogenic sprouting of three-dimensionally co-cultured HUVECs and DPSCs through VEGF-Ang-Tie2 signaling
Abstract
Background: Maintaining the stability and maturation of blood vessels is of paramount importance for the vessels to carry out their physiological function. Smooth muscle cells (SMCs), pericytes, and mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are involved in the maturation process of the newly formed vessels. The aim of this study was to investigate whether transforming growth factor beta 1 (TGF-β1) treatment could enhance pericyte-like properties of dental pulp stem cells (DPSCs) and how TGF-β1-treated DPSCs for 7 days (T-DPSCs) stabilize the newly formed blood vessels.
Methods: We utilized TGF-β1 to treat DPSCs for 1, 3, 5, and 7 days. Western blotting and immunofluorescence were used to analyze the expression of SMC markers. Functional contraction assay was conducted to assess the contractility of T-DPSCs. The effects of T-DPSC-conditioned media (T-DPSC-CM) on human umbilical vein endothelial cell (HUVEC) proliferation and migration were examined by MTT, wound healing, and trans-well migration assay. Most importantly, in vitro 3D co-culture spheroidal sprouting assay was used to investigate the regulating role of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-angiopoietin (Ang)-Tie2 signaling on angiogenic sprouting in 3D co-cultured spheroids of HUVECs and T-DPSCs. Angiopoietin 2 (Ang2) and VEGF were used to treat the co-cultured spheroids to explore their roles in angiogenic sprouting. Inhibitors for Tie2 and VEGFR2 were used to block Ang1/Tie2 and VFGF/VEGFR2 signaling.
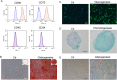
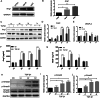
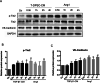
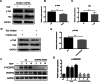
Results: Western blotting and immunofluorescence showed that the expression of SMC-specific markers (α-SMA and SM22α) were significantly increased after treatment with TGF-β1. Contractility of T-DPSCs was greater compared with that of DPSCs. T-DPSC-CM inhibited HUVEC migration. In vitro sprouting assay demonstrated that T-DPSCs enclosed HUVECs, resembling pericyte-like cells. Compared to co-culture with DPSCs, a smaller number of HUVEC sprouting was observed when co-cultured with T-DPSCs. VEGF and Ang2 co-stimulation significantly enhanced sprouting in HUVEC and T-DPSC co-culture spheroids, whereas VEGF or Ang2 alone exerted insignificant effects on HUVEC sprouting. Blocking Tie2 signaling reversed the sprouting inhibition by T-DPSCs, while blocking VEGF receptor (VEGFR) signaling boosted the sprouting inhibition by T-DPSCs.
Conclusions: This study revealed that TGF-β1 can induce DPSC differentiation into functional pericyte-like cells. T-DPSCs maintain vessel stability through Ang1/Tie2 and VEGF/VEGFR2 signaling.
Keywords: Ang1/Tie2 signaling; Angiogenesis; Dental pulp stem cells; Smooth muscle cells; Vessel stability.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures





References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

