Evaluation of intravitreal topotecan dose levels, toxicity and efficacy for retinoblastoma vitreous seeds: a preclinical and clinical study
- PMID: 33972235
- PMCID: PMC8788260
- DOI: 10.1136/bjophthalmol-2020-318529
Evaluation of intravitreal topotecan dose levels, toxicity and efficacy for retinoblastoma vitreous seeds: a preclinical and clinical study
Abstract
Background: Current melphalan-based intravitreal regimens for retinoblastoma (RB) vitreous seeds cause retinal toxicity. We assessed the efficacy and toxicity of topotecan monotherapy compared with melphalan in our rabbit model and patient cohort.
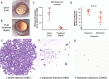
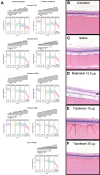
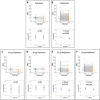
Methods: Rabbit experiments: empiric pharmacokinetics were determined following topotecan injection. For topotecan (15 μg or 30 µg), melphalan (12.5 µg) or saline, toxicity was evaluated by serial electroretinography (ERG) and histopathology, and efficacy against vitreous seed xenografts was measured by tumour cell reduction and apoptosis induction.
Patients: retrospective cohort study of 235 patients receiving 990 intravitreal injections of topotecan or melphalan.
Results: Intravitreal topotecan 30 µg (equals 60 µg in humans) achieved the IC90 across the rabbit vitreous. Three weekly topotecan injections (either 15 µg or 30 µg) caused no retinal toxicity in rabbits, whereas melphalan 12.5 µg (equals 25 µg in humans) reduced ERG amplitudes 42%-79%. Intravitreal topotecan 15 µg was equally effective to melphalan to treat WERI-Rb1 cell xenografts in rabbits (96% reduction for topotecan vs saline (p=0.004), 88% reduction for melphalan vs saline (p=0.004), topotecan vs melphalan, p=0.15). In our clinical study, patients received 881 monotherapy injections (48 topotecan, 833 melphalan). Patients receiving 20 µg or 30 µg topotecan demonstrated no significant ERG reductions; melphalan caused ERG reductions of 7.6 μV for every injection of 25 µg (p=0.03) or 30 µg (p<0.001). Most patients treated with intravitreal topotecan also received intravitreal melphalan at some point during their treatment course. Among those eyes treated exclusively with topotecan monotherapy, all eyes were salvaged.
Conclusions: Taken together, these experiments suggest that intravitreal topotecan monotherapy for the treatment of RB vitreous seeds is non-toxic and effective.
Keywords: animal models; efficacy; intravitreal chemotherapy; pharmacokinetics; retinoblastoma; topotecan; toxicity; vitreous seeds.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2022. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: ABD and DLF have a patent with Vanderbilt University Medical Center. ABD has received research funding from Spectrum Pharmaceuticals (now Acrotech Biopharma) through an investigator-initiated study separate from the data presented in this manuscript. None of the other authors has any conflicts of interest or financial disclosures.
Figures
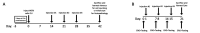

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
