Viral Proteases as Targets for Coronavirus Disease 2019 Drug Development
- PMID: 33972366
- PMCID: PMC8686716
- DOI: 10.1124/jpet.121.000688
Viral Proteases as Targets for Coronavirus Disease 2019 Drug Development
Abstract
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), continues to be a global threat since its emergence. Although several COVID-19 vaccines have become available, the prospective timeframe for achieving effective levels of vaccination across global populations remains uncertain. Moreover, the emergence of SARS-CoV-2 variants presents continuing potential challenges for future vaccination planning. Therefore, development of effective antiviral therapies continues to be an urgent unmet need for COVID-19. Successful antiviral regimens for the treatment of human immunodeficiency virus and hepatitis C virus infections have established viral proteases as validated targets for antiviral drug development. In this context, we review protease targets in drug development, currently available antiviral protease inhibitors, and therapeutic development efforts on SARS-CoV-2 main protease and papain-like protease. SIGNIFICANCE STATEMENT: Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) continues to be a global threat since its emergence. The development of effective antiviral therapeutics for COVID-19 remains an urgent and long-term need. Because viral proteases are validated drug targets, specific severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 protease inhibitors are critical therapeutics to be developed for treatment of COVID-19.
U.S. Government work not protected by U.S. copyright.
Figures
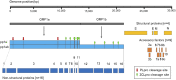
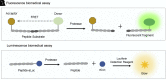
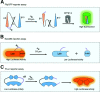
References
-
- Alexander SPH, Ball JK, Tsoleridis T (2020) Coronavirus (CoV) proteins (version 2020.5) in the IUPHAR/BPS Guide to Pharmacology Database. IUPHAR/BPS Guide to Pharmacology CITE 2020.
-
- Anand K, Ziebuhr J, Wadhwani P, Mesters JR, Hilgenfeld R (2003) Coronavirus main proteinase (3CLpro) structure: basis for design of anti-SARS drugs. Science 300:1763–1767. - PubMed
-
- Bartenschlager R, Lohmann V, Penin F (2013) The molecular and structural basis of advanced antiviral therapy for hepatitis C virus infection. Nat Rev Microbiol 11:482–496. - PubMed
-
- Berlin DA, Gulick RM, Martinez FJ (2020) Severe Covid-19. N Engl J Med 383:2451–2460. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

