The circadian clock ensures successful DNA replication in cyanobacteria
- PMID: 33972427
- PMCID: PMC8157973
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2022516118
The circadian clock ensures successful DNA replication in cyanobacteria
Abstract
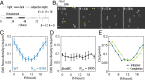
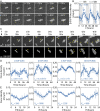
Disruption of circadian rhythms causes decreased health and fitness, and evidence from multiple organisms links clock disruption to dysregulation of the cell cycle. However, the function of circadian regulation for the essential process of DNA replication remains elusive. Here, we demonstrate that in the cyanobacterium Synechococcus elongatus, a model organism with the simplest known circadian oscillator, the clock generates rhythms in DNA replication to minimize the number of open replication forks near dusk that would have to complete after sunset. Metabolic rhythms generated by the clock ensure that resources are available early at night to support any remaining replication forks. Combining mathematical modeling and experiments, we show that metabolic defects caused by clock-environment misalignment result in premature replisome disassembly and replicative abortion in the dark, leaving cells with incomplete chromosomes that persist through the night. Our study thus demonstrates that a major function of this ancient clock in cyanobacteria is to ensure successful completion of genome replication in a cycling environment.
Keywords: DNA replication; cell cycle; circadian clock; cyanobacteria; mathematical modeling.
Copyright © 2021 the Author(s). Published by PNAS.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Investigating the Roles for Essential Genes in the Regulation of the Circadian Clock in Synechococcus elongatus Using CRISPR Interference.J Biol Rhythms. 2024 Jun;39(3):308-317. doi: 10.1177/07487304241228333. Epub 2024 Feb 15. J Biol Rhythms. 2024. PMID: 38357890
-
Discrete gene replication events drive coupling between the cell cycle and circadian clocks.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016 Apr 12;113(15):4063-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1507291113. Epub 2016 Mar 28. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016. PMID: 27035936 Free PMC article.
-
The Kai-Protein Clock-Keeping Track of Cyanobacteria's Daily Life.Subcell Biochem. 2019;93:359-391. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-28151-9_12. Subcell Biochem. 2019. PMID: 31939158 Review.
-
The cyanobacterial circadian clock couples to pulsatile processes using pulse amplitude modulation.Curr Biol. 2024 Dec 16;34(24):5796-5803.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2024.10.047. Epub 2024 Nov 25. Curr Biol. 2024. PMID: 39591971
-
Circadian timekeeping in Neurospora crassa and Synechococcus elongatus.Essays Biochem. 2011 Jun 30;49(1):37-51. doi: 10.1042/bse0490037. Essays Biochem. 2011. PMID: 21819383 Review.
Cited by
-
A topological mechanism for robust and efficient global oscillations in biological networks.Nat Commun. 2024 Jul 31;15(1):6453. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-50510-x. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39085205 Free PMC article.
-
Synchronization of the circadian clock to the environment tracked in real time.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023 Mar 28;120(13):e2221453120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2221453120. Epub 2023 Mar 20. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023. PMID: 36940340 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism for the Generation of Robust Circadian Oscillations through Ultransensitivity and Differential Binding Affinity.J Phys Chem B. 2021 Oct 14;125(40):11179-11187. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcb.1c05915. Epub 2021 Oct 5. J Phys Chem B. 2021. PMID: 34609867 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic Responses of Metabolically Active Limnospira indica Strain PCC 8005 Exposed to γ-Radiation during Its Lifecycle.Microorganisms. 2021 Jul 30;9(8):1626. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms9081626. Microorganisms. 2021. PMID: 34442705 Free PMC article.
-
Clocks at a snail pace: biological rhythms in terrestrial gastropods.PeerJ. 2024 Oct 29;12:e18318. doi: 10.7717/peerj.18318. eCollection 2024. PeerJ. 2024. PMID: 39494278 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Dunlap J. C., Molecular bases for circadian clocks. Cell 96, 271–290 (1999). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

