A modular computational framework for medical digital twins
- PMID: 33972437
- PMCID: PMC8157963
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2024287118
A modular computational framework for medical digital twins
Abstract
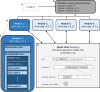
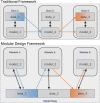
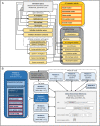
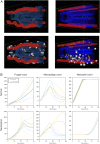
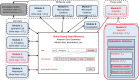
This paper presents a modular software design for the construction of computational modeling technology that will help implement precision medicine. In analogy to a common industrial strategy used for preventive maintenance of engineered products, medical digital twins are computational models of disease processes calibrated to individual patients using multiple heterogeneous data streams. They have the potential to help improve diagnosis, prognosis, and personalized treatment for a wide range of medical conditions. Their large-scale development relies on both mechanistic and data-driven techniques and requires the integration and ongoing update of multiple component models developed across many different laboratories. Distributed model building and integration requires an open-source modular software platform for the integration and simulation of models that is scalable and supports a decentralized, community-based model building process. This paper presents such a platform, including a case study in an animal model of a respiratory fungal infection.
Keywords: medical digital twin; modular design; multiscale computational model.
Copyright © 2021 the Author(s). Published by PNAS.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures

References
-
- Kovatchev B. P., Brown S. A., Beck R. W., Multicenter trial of closed-loop control in type 1 diabetes. Reply. N. Engl. J. Med. 382, 578 (2020). - PubMed
-
- Hose D. R., et al. ., Cardiovascular models for personalised medicine: Where now and where next? Med. Eng. Phys. 72, 38–48 (2019). - PubMed
-
- Lauzeral N., et al. ., A model order reduction approach to create patient-specific mechanical models of human liver in computational medicine applications. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 170, 95–106 (2019). - PubMed
-
- Hirschvogel M., Jagschies L., Maier A., Wildhirt S. M., Gee M. W., An in silico twin for epicardial augmentation of the failing heart. Int. J. Numer. Methods Biomed. Eng. 35, e3233 (2019). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

