Post-Translational Modifications in Transcription Factors that Determine T Helper Cell Differentiation
- PMID: 33972470
- PMCID: PMC8175150
- DOI: 10.14348/molcells.2021.0057
Post-Translational Modifications in Transcription Factors that Determine T Helper Cell Differentiation
Abstract
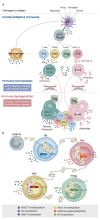
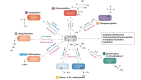
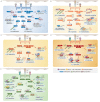
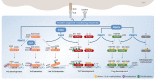
CD4+ T helper (Th) cells play a crucial role in the modulation of innate and adaptive immune responses through the differentiation of Th precursor cells into several subsets, including Th1, Th2, Th17, and regulatory T (Treg) cells. Effector Th and Treg cells are distinguished by the production of signature cytokines and are important for eliminating intracellular and extracellular pathogens and maintaining immune homeostasis. Stimulation of naïve Th cells by T cell receptor and specific cytokines activates master transcription factors and induces lineage specification during the differentiation of Th cells. The master transcription factors directly activate the transcription of signature cytokine genes and also undergo post-translational modifications to fine-tune cytokine production and maintain immune balance through cross-regulation with each other. This review highlights the post-translational modifications of master transcription factors that control the differentiation of effector Th and Treg cells and provides additional insights on the immune regulation mediated by protein arginine-modifying enzymes in effector Th cells.
Keywords: CD4 T cell differentiation; arginine-modifying enzyme; effector Th and Treg cell; master regulatory transcription factor; post-translational modifications.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Mechanisms of Effector Th Cell Responses Contribute to Treg Cell Function: New Insights into Pathogenesis and Therapy of Asthma.Front Immunol. 2022 Jul 11;13:862866. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.862866. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35898499 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Complex interactions of transcription factors in mediating cytokine biology in T cells.Immunol Rev. 2014 Sep;261(1):141-56. doi: 10.1111/imr.12199. Immunol Rev. 2014. PMID: 25123282 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CD4 T Helper Cell Subsets and Related Human Immunological Disorders.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Oct 28;21(21):8011. doi: 10.3390/ijms21218011. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33126494 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development, regulation and functional capacities of Th17 cells.Semin Immunopathol. 2010 Mar;32(1):3-16. doi: 10.1007/s00281-009-0187-y. Epub 2010 Jan 27. Semin Immunopathol. 2010. PMID: 20107806 Review.
-
The role of protein modifications of T-bet in cytokine production and differentiation of T helper cells.J Immunol Res. 2014;2014:589672. doi: 10.1155/2014/589672. Epub 2014 May 13. J Immunol Res. 2014. PMID: 24901011 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Protein arginine methyltransferases as regulators of cellular stress.Exp Neurol. 2025 Feb;384:115060. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2024.115060. Epub 2024 Nov 17. Exp Neurol. 2025. PMID: 39551462 Free PMC article. Review.
-
USP28 protects development of inflammation in mouse intestine by regulating STAT5 phosphorylation and IL22 production in T lymphocytes.Front Immunol. 2024 Jul 15;15:1401949. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1401949. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39076972 Free PMC article.
-
Deciphering the dynamic code: DNA recognition by transcription factors in the ever-changing genome.Transcription. 2024 Jun-Oct;15(3-5):114-138. doi: 10.1080/21541264.2024.2379161. Epub 2024 Jul 20. Transcription. 2024. PMID: 39033307 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current Understanding of Cytotoxic T Lymphocyte Antigen-4 (CTLA-4) Signaling in T-Cell Biology and Disease Therapy.Mol Cells. 2022 Aug 31;45(8):513-521. doi: 10.14348/molcells.2022.2056. Epub 2022 Jul 27. Mol Cells. 2022. PMID: 35950451 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bio-Pathological Functions of Posttranslational Modifications of Histological Biomarkers in Breast Cancer.Molecules. 2024 Sep 2;29(17):4156. doi: 10.3390/molecules29174156. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39275004 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

