Post-Translational Modifications in Transcription Factors that Determine T Helper Cell Differentiation
- PMID: 33972470
- PMCID: PMC8175150
- DOI: 10.14348/molcells.2021.0057
Post-Translational Modifications in Transcription Factors that Determine T Helper Cell Differentiation
Abstract
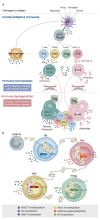
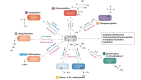
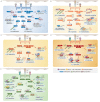
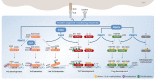
CD4+ T helper (Th) cells play a crucial role in the modulation of innate and adaptive immune responses through the differentiation of Th precursor cells into several subsets, including Th1, Th2, Th17, and regulatory T (Treg) cells. Effector Th and Treg cells are distinguished by the production of signature cytokines and are important for eliminating intracellular and extracellular pathogens and maintaining immune homeostasis. Stimulation of naïve Th cells by T cell receptor and specific cytokines activates master transcription factors and induces lineage specification during the differentiation of Th cells. The master transcription factors directly activate the transcription of signature cytokine genes and also undergo post-translational modifications to fine-tune cytokine production and maintain immune balance through cross-regulation with each other. This review highlights the post-translational modifications of master transcription factors that control the differentiation of effector Th and Treg cells and provides additional insights on the immune regulation mediated by protein arginine-modifying enzymes in effector Th cells.
Keywords: CD4 T cell differentiation; arginine-modifying enzyme; effector Th and Treg cell; master regulatory transcription factor; post-translational modifications.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

