Innate Lymphoid Cells in Tissue Homeostasis and Disease Pathogenesis
- PMID: 33972473
- PMCID: PMC8175152
- DOI: 10.14348/molcells.2021.0053
Innate Lymphoid Cells in Tissue Homeostasis and Disease Pathogenesis
Abstract
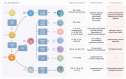
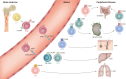
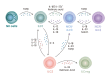
Innate lymphoid cells (ILCs) are the most recently discovered family of innate immune cells. ILCs can be categorized into three groups on the basis of the transcription factors that direct their functions and the cytokines they produce. Notably, these functions parallel the effector functions of T lymphocytes. ILCs play a frontline role in host defense and tissue homeostasis by responding rapidly to environmental factors, conducting effector responses in a tissue-specific manner, and interacting with hematopoietic and non-hematopoietic cells throughout the body. Moreover, recent studies reveal that ILCs are involved in development of various inflammatory diseases, such as respiratory diseases, autoimmune diseases, or cancer. In this review, we discuss the recent findings regarding the biology of ILCs in health and inflammatory diseases.
Keywords: development; homeostasis; inflammation; innate lymphoid cells; plasticity; tropism.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pathological and therapeutic roles of innate lymphoid cells in diverse diseases.Arch Pharm Res. 2017 Nov;40(11):1249-1264. doi: 10.1007/s12272-017-0974-2. Epub 2017 Oct 14. Arch Pharm Res. 2017. PMID: 29032487 Review.
-
Characteristics of innate lymphoid cells (ILCs) and their role in immunological disorders (an update).Cell Immunol. 2015 Nov-Dec;298(1-2):66-76. doi: 10.1016/j.cellimm.2015.09.006. Epub 2015 Sep 26. Cell Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26429626 Review.
-
Molecular characteristics and possible functions of innate lymphoid cells in the uterus and gut.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2020 Apr;52:15-24. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2019.11.003. Epub 2019 Nov 15. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2020. PMID: 31771906 Review.
-
Innate lymphoid cells are pivotal actors in allergic, inflammatory and autoimmune diseases.Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2015;11(8):885-95. doi: 10.1586/1744666X.2015.1050382. Epub 2015 May 25. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26004582 Review.
-
Human innate lymphoid cells.Blood. 2014 Jul 31;124(5):700-9. doi: 10.1182/blood-2013-11-427781. Epub 2014 Apr 28. Blood. 2014. PMID: 24778151 Review.
Cited by
-
Wound-Induced Hair Follicle Neogenesis as a Promising Approach for Hair Regeneration.Mol Cells. 2023 Oct 31;46(10):573-578. doi: 10.14348/molcells.2023.0071. Epub 2023 Aug 31. Mol Cells. 2023. PMID: 37650216 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unique adipose tissue invariant natural killer T cell subpopulations control adipocyte turnover in mice.Nat Commun. 2023 Dec 21;14(1):8512. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-44181-3. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 38129377 Free PMC article.
-
Versatile roles of innate lymphoid cells at the mucosal barrier: from homeostasis to pathological inflammation.Exp Mol Med. 2023 Sep;55(9):1845-1857. doi: 10.1038/s12276-023-01022-z. Epub 2023 Sep 11. Exp Mol Med. 2023. PMID: 37696896 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mesenchymal Stem Cells Suppress Severe Asthma by Directly Regulating Th2 Cells and Type 2 Innate Lymphoid Cells.Mol Cells. 2021 Aug 31;44(8):580-590. doi: 10.14348/molcells.2021.0101. Mol Cells. 2021. PMID: 34462397 Free PMC article.
-
(Multi-) omics studies of ILC2s in inflammation and metabolic diseases.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024 Oct 28;12:1473616. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1473616. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024. PMID: 39529633 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bal S.M., Bernink J.H., Nagasawa M., Groot J., Shikhagaie M.M., Golebski K., van Drunen C.M., Lutter R., Jonkers R.E., Hombrink P., et al. IL-1beta, IL-4 and IL-12 control the fate of group 2 innate lymphoid cells in human airway inflammation in the lungs. Nat. Immunol. 2016;17:636–645. - PubMed
-
- Bernink J.H., Krabbendam L., Germar K., de Jong E., Gronke K., Kofoed-Nielsen M., Munneke J.M., Hazenberg M.D., Villaudy J., Buskens C.J. Interleukin-12 and-23 control plasticity of CD127+ group 1 and group 3 innate lymphoid cells in the intestinal lamina propria. Immunity. 2015;43:146–160. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2015.06.019. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

