Th17 cells contribute to combination MEK inhibitor and anti-PD-L1 therapy resistance in KRAS/p53 mutant lung cancers
- PMID: 33972557
- PMCID: PMC8110980
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-021-22875-w
Th17 cells contribute to combination MEK inhibitor and anti-PD-L1 therapy resistance in KRAS/p53 mutant lung cancers
Abstract
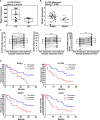
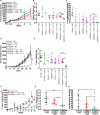
Understanding resistance mechanisms to targeted therapies and immune checkpoint blockade in mutant KRAS lung cancers is critical to developing novel combination therapies and improving patient survival. Here, we show that MEK inhibition enhanced PD-L1 expression while PD-L1 blockade upregulated MAPK signaling in mutant KRAS lung tumors. Combined MEK inhibition with anti-PD-L1 synergistically reduced lung tumor growth and metastasis, but tumors eventually developed resistance to sustained combinatorial therapy. Multi-platform profiling revealed that resistant lung tumors have increased infiltration of Th17 cells, which secrete IL-17 and IL-22 cytokines to promote lung cancer cell invasiveness and MEK inhibitor resistance. Antibody depletion of IL-17A in combination with MEK inhibition and PD-L1 blockade markedly reduced therapy-resistance in vivo. Clinically, increased expression of Th17-associated genes in patients treated with PD-1 blockade predicted poorer overall survival and response in melanoma and predicated poorer response to anti-PD1 in NSCLC patients. Here we show a triple combinatorial therapeutic strategy to overcome resistance to combined MEK inhibitor and PD-L1 blockade.
Conflict of interest statement
D.L.G. declares advisory board work for Janssen, AstraZeneca, GlaxoSmithKline, and Sanofi. D.L.G. receives research grant funding from AstraZeneca, Janssen, Astellas, Ribon Therapeutics, NGM Therapeutics, and Takeda. L.A.B. declares consulting work for AstraZeneca, AbbVie, GenMab, BergenBio, Pharma Mar, SA. L.A.B. receives research grant funding from AbbVie, AstraZeneca, GenMab, Tolero Pharmaceuticals. All other authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures





References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

