Allopurinol ameliorates high fructose diet induced hepatic steatosis in diabetic rats through modulation of lipid metabolism, inflammation, and ER stress pathway
- PMID: 33972568
- PMCID: PMC8110790
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-88872-7
Allopurinol ameliorates high fructose diet induced hepatic steatosis in diabetic rats through modulation of lipid metabolism, inflammation, and ER stress pathway
Abstract
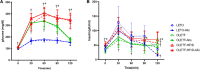
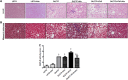
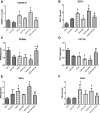
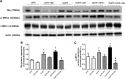
Excess fructose consumption contributes to development obesity, metabolic syndrome, and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Uric acid (UA), a metabolite of fructose metabolism, may have a direct role in development of NAFLD, with unclear mechanism. This study aimed to evaluate role of fructose and UA in NAFLD and explore mechanisms of allopurinol (Allo, a UA lowering medication) on NAFLD in Otsuka Long-Evans Tokushima Fatty (OLETF) rats fed a high fructose diet (HFrD), with Long-Evans Tokushima Otsuka (LETO) rats used as a control. There were six groups: LETO, LETO-Allo, OLETF, OLETF-Allo, OLETF-HFrD, and OLETF-HFrD-Allo. HFrD significantly increased body weight, epididymal fat weight, and serum concentrations of UA, cholesterol, triglyceride, HbA1c, hepatic enzymes, HOMA-IR, fasting insulin, and two hour-glucose after intraperitoneal glucose tolerance tests, as well as NAFLD activity score of liver, compared to the OLETF group. Allopurinol treatment significantly reduced hepatic steatosis, epididymal fat, serum UA, HOMA-IR, hepatic enzyme levels, and cholesterol in the OLETF-HFrD-Allo group. Additionally, allopurinol significantly downregulated expression of lipogenic genes, upregulated lipid oxidation genes, downregulated hepatic pro-inflammatory cytokine genes, and decreased ER-stress induced protein expression, in comparison with the OLETF-HFrD group. In conclusion, allopurinol ameliorates HFrD-induced hepatic steatosis through modulation of hepatic lipid metabolism, inflammation, and ER stress pathway. UA may have a direct role in development of fructose-induced hepatic steatosis, and allopurinol could be a candidate for prevention or treatment of NAFLD.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

