Improving radiologist's ability in identifying particular abnormal lesions on mammograms through training test set with immediate feedback
- PMID: 33972611
- PMCID: PMC8110801
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-89214-3
Improving radiologist's ability in identifying particular abnormal lesions on mammograms through training test set with immediate feedback
Abstract
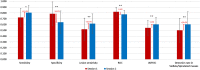
It has been shown that there are differences in diagnostic accuracy of cancer detection on mammograms, from below 50% in developing countries to over 80% in developed world. One previous study reported that radiologists from a population in Asia displayed a low mammographic cancer detection of 48% compared with over 80% in developed countries, and more importantly, that most lesions missed by these radiologists were spiculated masses or stellate lesions. The aim of this study was to explore the performance of radiologists after undertaking a training test set which had been designed to improve the capability in detecting a specific type of cancers on mammograms. Twenty-five radiologists read two sets of 60 mammograms in a standardized mammogram reading room. The first test set focused on stellate or spiculated masses. When radiologists completed the first set, the system displayed immediate feedback to the readers comparing their performances in each case with the truth of cancer cases and cancer types so that the readers could identify individual-based errors. Later radiologists were asked to read the second set of mammograms which contained different types of cancers including stellate/spiculated masses, asymmetric density, calcification, discrete mass and architectural distortion. Case sensitivity, lesion sensitivity, specificity, receiver operating characteristics (ROC) and Jackknife alternative free-response receiver operating characteristics (JAFROC) were calculated for each participant and their diagnostic accuracy was compared between two sessions. Results showed significant improvement among radiologists in case sensitivity (+ 11.4%; P < 0.05), lesion sensitivity (+ 18.7%; P < 0.01) and JAFROC (+ 11%; P < 0.01) in the second set compared with the first set. The increase in diagnostic accuracy was also recorded in the detection of stellate/spiculated mass (+ 20.6%; P < 0.05). This indicated that the performance of radiologists in detecting malignant lesions on mammograms can be improved if an appropriate training intervention is applied after the readers' weakness and strength are identified.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests in this study.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Look how far we have come: BREAST cancer detection education on the international stage.Front Oncol. 2023 Jan 4;12:1023714. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1023714. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36686760 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Improvement of Cancer Detection on Mammograms via BREAST Test Sets.Acad Radiol. 2019 Dec;26(12):e341-e347. doi: 10.1016/j.acra.2018.12.017. Epub 2019 Feb 28. Acad Radiol. 2019. PMID: 30826148
-
Reader characteristics and mammogram features associated with breast imaging reporting scores.Br J Radiol. 2020 Oct 1;93(1114):20200363. doi: 10.1259/bjr.20200363. Epub 2020 Aug 5. Br J Radiol. 2020. PMID: 32730088 Free PMC article.
-
Optimizing Radiological Education: The Role of Learning Spacing via Test sets in Enhancing Diagnostic Proficiency in Breast Screening Readers.Acad Radiol. 2024 Oct;31(10):4261-4271. doi: 10.1016/j.acra.2024.06.039. Epub 2024 Jul 23. Acad Radiol. 2024. PMID: 39048496
-
Utility of Supplemental Training to Improve Radiologist Performance in Breast Cancer Screening: A Literature Review.J Am Coll Radiol. 2019 Nov;16(11):1528-1546. doi: 10.1016/j.jacr.2019.04.016. Epub 2019 Jun 24. J Am Coll Radiol. 2019. PMID: 31247156
Cited by
-
Surgical and Radiology Trainees' Proficiency in Reading Mammograms: the Importance of Education for Cancer Localisation.J Cancer Educ. 2024 Apr;39(2):186-193. doi: 10.1007/s13187-023-02393-7. Epub 2023 Dec 15. J Cancer Educ. 2024. PMID: 38100062 Free PMC article.
-
The Impact of Prior Mammograms on the Diagnostic Performance of Radiologists in Early Breast Cancer Detection: A Focus on Breast Density, Lesion Features and Vendors Using Wholly Digital Screening Cases.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Feb 20;15(4):1339. doi: 10.3390/cancers15041339. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36831680 Free PMC article.
-
Look how far we have come: BREAST cancer detection education on the international stage.Front Oncol. 2023 Jan 4;12:1023714. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1023714. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36686760 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Using Radiomics-Based Machine Learning to Create Targeted Test Sets to Improve Specific Mammography Reader Cohort Performance: A Feasibility Study.J Pers Med. 2023 May 24;13(6):888. doi: 10.3390/jpm13060888. J Pers Med. 2023. PMID: 37373877 Free PMC article.
-
Learning effects in visual grading assessment of model-based reconstruction algorithms in abdominal Computed Tomography.Eur J Radiol Open. 2023 May 6;10:100490. doi: 10.1016/j.ejro.2023.100490. eCollection 2023. Eur J Radiol Open. 2023. PMID: 37207049 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bray F, et al. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018;68:394–424. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical