Factors contributing to discrepant estimated glomerular filtration values measured by creatinine and cystatin C in patients with rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 33972623
- PMCID: PMC8110572
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-89303-3
Factors contributing to discrepant estimated glomerular filtration values measured by creatinine and cystatin C in patients with rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
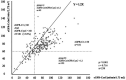
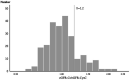
This study aimed to clarify the factors underlying the discrepancy that has been noted between estimated glomerular filtration ratio (eGFR) measured using serum creatinine (Cr) and eGFR using serum cystatin C (CysC) in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and to identify those patients whose renal function should be evaluated using CysC. We retrospectively evaluated clinical features, disease activity, Steinbrocker radiological staging, and co-morbidities (diabetes mellitus, hypertension, dyslipidemia) in 238 RA patients. eGFR using serum creatinine (eGFR-Cr) and eGFR using serum cystatin C (eGFR-CysC) were calculated using the new Japanese coefficient-modified Modification of Diet in Renal Disease study equation. To clarify the cause(s) of differences of 20% or more between the two eGFRs, we divided our RA patients into Group A (eGFR-Cr/eGFR-CysC ≥ 1.2) and Group B (eGFR-Cr/eGFR-CysC < 1.2), and searched for factors independently related to Group A. Forty-five patients (18.9%) were assigned to Group A, and 193 (81.1%) to Group B. BMI (Odds Ratio [OR] 0.820, 95% confidence interval [CI] 0.675-0.996), Hb (OR 0.633, 95% CI 0.433-0.926), CK (OR 0.773 per 10 units, 95% CI 0.644-0.933), NSAID use (OR 0.099, 95% CI 0.020-0.494), diabetes mellitus (OR 6.024, 95% CI 1.508-24.390) and stage 4 Steinbrocker radiological stage (OR 10.309, 95% CI 2.994-35.714) were identified as independent relevant factors for Group A by a multifactorial analysis. Renal function in RA patients with low BMI, diabetes, anemia and low CK may be overestimated using eGFR-Cr alone, and such patients need to be evaluated using eGFR-CysC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cystatin C is a sensitive marker for detecting a reduced glomerular filtration rate when assessing chronic kidney disease in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and secondary amyloidosis.Scand J Rheumatol. 2010;39(1):33-7. doi: 10.3109/03009740903042402. Scand J Rheumatol. 2010. PMID: 20132068
-
The Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration cystatin C (CKD-EPI-CysC) equation has an independent prognostic value for overall survival in newly diagnosed patients with symptomatic multiple myeloma; is it time to change from MDRD to CKD-EPI-CysC equations?Eur J Haematol. 2013 Oct;91(4):347-55. doi: 10.1111/ejh.12164. Epub 2013 Aug 17. Eur J Haematol. 2013. PMID: 23829647
-
Comparison of estimated GFR equations based on serum cystatin C alone and in combination with serum creatinine in patients with coronary artery disease.Anatol J Cardiol. 2015 Jul;15(7):571-6. doi: 10.5152/akd.2014.5535. Epub 2014 Jul 16. Anatol J Cardiol. 2015. PMID: 25537999 Free PMC article.
-
Estimating renal function in children: a new GFR-model based on serum cystatin C and body cell mass.Dan Med J. 2012 Jul;59(7):B4486. Dan Med J. 2012. PMID: 22759853 Review.
-
Diagnostic test accuracy of serum creatinine and cystatin C-based index for sarcopenia: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Age Ageing. 2024 Jan 2;53(1):afad252. doi: 10.1093/ageing/afad252. Age Ageing. 2024. PMID: 38251741
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

