Novel AI driven approach to classify infant motor functions
- PMID: 33972661
- PMCID: PMC8110753
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-89347-5
Novel AI driven approach to classify infant motor functions
Abstract
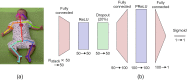
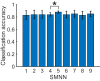
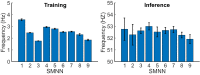
The past decade has evinced a boom of computer-based approaches to aid movement assessment in early infancy. Increasing interests have been dedicated to develop AI driven approaches to complement the classic Prechtl general movements assessment (GMA). This study proposes a novel machine learning algorithm to detect an age-specific movement pattern, the fidgety movements (FMs), in a prospectively collected sample of typically developing infants. Participants were recorded using a passive, single camera RGB video stream. The dataset of 2800 five-second snippets was annotated by two well-trained and experienced GMA assessors, with excellent inter- and intra-rater reliabilities. Using OpenPose, the infant full pose was recovered from the video stream in the form of a 25-points skeleton. This skeleton was used as input vector for a shallow multilayer neural network (SMNN). An ablation study was performed to justify the network's architecture and hyperparameters. We show for the first time that the SMNN is sufficient to discriminate fidgety from non-fidgety movements in a sample of age-specific typical movements with a classification accuracy of 88%. The computer-based solutions will complement original GMA to consistently perform accurate and efficient screening and diagnosis that may become universally accessible in daily clinical practice in the future.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
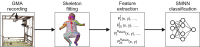

Similar articles
-
Characteristics of general movements in preterm infants assessed by computer-based video analysis.Physiother Theory Pract. 2018 Apr;34(4):286-292. doi: 10.1080/09593985.2017.1391908. Epub 2017 Oct 24. Physiother Theory Pract. 2018. PMID: 29064734
-
Computer-based video analysis identifies infants with absence of fidgety movements.Pediatr Res. 2017 Oct;82(4):665-670. doi: 10.1038/pr.2017.121. Epub 2017 Jul 26. Pediatr Res. 2017. PMID: 28745715
-
Using computer-based video analysis in the study of fidgety movements.Early Hum Dev. 2009 Sep;85(9):541-7. doi: 10.1016/j.earlhumdev.2009.05.003. Epub 2009 May 22. Early Hum Dev. 2009. PMID: 19464127
-
The future of General Movement Assessment: The role of computer vision and machine learning - A scoping review.Res Dev Disabil. 2021 Mar;110:103854. doi: 10.1016/j.ridd.2021.103854. Epub 2021 Feb 8. Res Dev Disabil. 2021. PMID: 33571849 Free PMC article.
-
Fidgety movements - tiny in appearance, but huge in impact.J Pediatr (Rio J). 2016 May-Jun;92(3 Suppl 1):S64-70. doi: 10.1016/j.jped.2015.12.003. Epub 2016 Mar 17. J Pediatr (Rio J). 2016. PMID: 26997356 Review.
Cited by
-
Towards universal early screening for cerebral palsy: a roadmap for automated General Movements Assessment.EClinicalMedicine. 2025 Jul 22;86:103379. doi: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2025.103379. eCollection 2025 Aug. EClinicalMedicine. 2025. PMID: 40735348 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Machine learning approaches to evaluate infants' general movements in the writhing stage-a pilot study.Sci Rep. 2024 Feb 24;14(1):4522. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-54297-1. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38402234 Free PMC article.
-
The Importance of Monitoring Neurodevelopmental Outcomes for Preterm Infants: A Comparison of the AIMS, GMA, Pull to Sit Maneuver and ASQ-3.J Clin Med. 2022 Oct 26;11(21):6295. doi: 10.3390/jcm11216295. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 36362524 Free PMC article.
-
Digitally assisted diagnostics of autism spectrum disorder.Front Psychiatry. 2023 Feb 1;14:1066284. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2023.1066284. eCollection 2023. Front Psychiatry. 2023. PMID: 36816410 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Deep learning empowered sensor fusion boosts infant movement classification.Commun Med (Lond). 2025 Jan 14;5(1):16. doi: 10.1038/s43856-024-00701-w. Commun Med (Lond). 2025. PMID: 39809877 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

