Sulfopin is a covalent inhibitor of Pin1 that blocks Myc-driven tumors in vivo
- PMID: 33972797
- PMCID: PMC9119696
- DOI: 10.1038/s41589-021-00786-7
Sulfopin is a covalent inhibitor of Pin1 that blocks Myc-driven tumors in vivo
Abstract
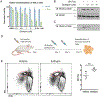
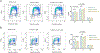
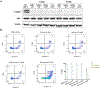
The peptidyl-prolyl isomerase, Pin1, is exploited in cancer to activate oncogenes and inactivate tumor suppressors. However, despite considerable efforts, Pin1 has remained an elusive drug target. Here, we screened an electrophilic fragment library to identify covalent inhibitors targeting Pin1's active site Cys113, leading to the development of Sulfopin, a nanomolar Pin1 inhibitor. Sulfopin is highly selective, as validated by two independent chemoproteomics methods, achieves potent cellular and in vivo target engagement and phenocopies Pin1 genetic knockout. Pin1 inhibition had only a modest effect on cancer cell line viability. Nevertheless, Sulfopin induced downregulation of c-Myc target genes, reduced tumor progression and conferred survival benefit in murine and zebrafish models of MYCN-driven neuroblastoma, and in a murine model of pancreatic cancer. Our results demonstrate that Sulfopin is a chemical probe suitable for assessment of Pin1-dependent pharmacology in cells and in vivo, and that Pin1 warrants further investigation as a potential cancer drug target.
© 2021. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature America, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
N.S.G. is a Scientific Founder and member of the Scientific Advisory Board (SAB) of C4, Jengu, Inception, Larkspur, Syros, Soltego, Gatekeeper and Petra Pharmaceuticals and has received research funding from Novartis, Astellas, Taiho and Deerfield. N.L. is a member of the SAB of Totus medicines and Monte Rosa Therapeutics and has received research support from Teva and Pfizer. J.A.M. has received support through sponsored research agreements with AstraZeneca and Vertex. J.A.M. serves on the SAB of 908 Devices. C.M.B. is an employee of AstraZeneca. C.D., B.J.P., D.Z., S.H., X.L., K.P.L., X.Z.Z., T.L., N.S.G. and N.L. are inventors on a patent application related to the inhibitors described in this manuscript (no. PCT/IL2020/050043).
Figures


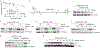
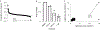
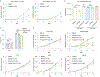
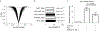

Comment in
-
Pinning down an elusive target.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2021 Jul;20(7):508. doi: 10.1038/d41573-021-00092-w. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2021. PMID: 34040180 No abstract available.
References
-
- Pawson T & Scott JD Protein phosphorylation in signaling—50 years and counting. Trends Biochem. Sci 30, 286–290 (2005). - PubMed
-
- Lu KP & Zhou XZ The prolyl isomerase PIN1: a pivotal new twist in phosphorylation signalling and disease. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol 8, 904–916 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Ryo A, Nakamura M, Wulf G, Liou YC & Lu KP Pin1 regulates turnover and subcellular localization of beta-catenin by inhibiting its interaction with APC. Nat. Cell Biol 3, 793–801 (2001). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- C34648/A18339/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- 28278/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- T32 GM095450/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA233800/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA186241/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- C34648/A14610/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- P41 GM103403/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- F31 CA225066/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA205153/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007306/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA196228/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM135301/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

