The antibacterial activity of peptide dendrimers and polymyxin B increases sharply above pH 7.4
- PMID: 33972964
- PMCID: PMC8186529
- DOI: 10.1039/d1cc01838h
The antibacterial activity of peptide dendrimers and polymyxin B increases sharply above pH 7.4
Abstract
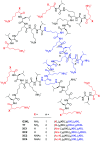
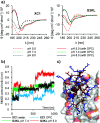
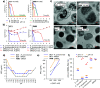
pH-activity profiling reveals that antimicrobial peptide dendrimers (AMPDs) kill Klebsiella pneumoniae and Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) at pH = 8.0, against which they are inactive at pH = 7.4, due to stronger electrostatic binding to bacterial cells at higher pH. A similar effect occurs with polymyxin B and might be general for polycationic antimicrobials.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

