Three-year effectiveness and safety of the XEN gel stent as a solo procedure or in combination with phacoemulsification in open-angle glaucoma: a multicentre study
- PMID: 33973370
- PMCID: PMC9290976
- DOI: 10.1111/aos.14886
Three-year effectiveness and safety of the XEN gel stent as a solo procedure or in combination with phacoemulsification in open-angle glaucoma: a multicentre study
Abstract
Purpose: To assess the 3-year effectiveness and safety of the XEN gel stent implanted ab interno in open-angle glaucoma (OAG).
Methods: This study was a multicentre, retrospective chart review of consecutive patients with OAG who underwent ab-interno gel stent placement alone or combined with phacoemulsification between 1 January 2014 and 1 October 2015. Outcome measures included mean changes in intraocular pressure (IOP) and IOP-lowering medication count from medicated baseline at 1, 2, 3 (primary outcome) and 4 years (if available) postimplantation. Intraoperative complications, adverse events of special interest (AESIs) and secondary surgical interventions (SSIs) were recorded.
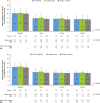
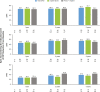
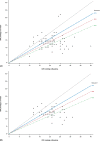
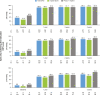
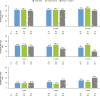
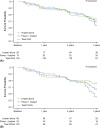
Results: The safety and effectiveness populations included 212 eyes (primary and secondary) and 174 eyes (primary), respectively. Mean IOP and medication decreased from 20.7 mmHg and 2.5 at baseline (n = 163 primary/first implanted eyes) to 13.9 mmHg and 1.1 medications (n = 76) at 3 years postimplantation, respectively. Mean changes from baseline in IOP (-5.6, -6.2 and -6.6 mmHg) and IOP-lowering medication count (-1.8, -1.6 and -1.4) were statistically significant at 1, 2 and 3 years postimplantation, respectively. Results appeared comparable when implantation was performed with (n = 76) or without (n = 98) phacoemulsification. In primary eyes with 4-year IOP and medication count data (n = 27), mean IOP was 14.0 mmHg on 1.3 medications at 4 years postimplantation. Fifteen (7.1%) eyes had intraoperative complications, 31 (14.6%) experienced 46 postoperative AESIs, and 26 (12.3%) required SSI.
Conclusion: The gel stent effectively lowered IOP and IOP-lowering medication count over 3 years, with a predictable and acceptable safety profile, when implanted via the traditional ab-interno technique.
Keywords: MIGS; XEN; gel stent; glaucoma; implant; intraocular pressure.
© 2021 AbbVie Inc. Acta Ophthalmologica published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Acta Ophthalmologica Scandinavica Foundation.
Figures
References
-
- Allergan (2016): Directions for Use for the XEN•45 Glaucoma Treatment System. Retrieved from: https://allergan‐web‐cdn‐prod.azureedge.net/allergan/allergannewzealand/.... Accessed on April 21, 2021.
-
- Allergan (2017): Directions for Use for the XEN® Glaucoma Treatment System. Retrieved from: https://allergan‐web‐cdn‐prod.azureedge.net/actavis/actavis/media/allerg.... Accessed on June 9, 2020.
-
- American Academy of Ophthalmology (2020): Preferred Practice Patterns−Primary open‐angle glaucoma. Available at: http://www.aaojournal.org/article/S0161‐6420(15)01276‐2/pdf. Accessed on August 3, 2020.
-
- Caprioli J, Kim JH, Friedman DS et al. (2015): Special commentary: Supporting innovation for safe and effective minimally invasive glaucoma surgery: Summary of a joint meeting of the American Glaucoma Society and the Food and Drug Administration, Washington, DC, February 26, 2014. Ophthalmology 122: 1795–1801. - PubMed
-
- European Glaucoma Society (2020): Terminology and guidelines for glaucoma (4th edition). Available at https://bjo.bmj.com/content/bjophthalmol/101/4/1.full.pdf. Accessed on August 3, 2020.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

