Innovations in Biomaterial Design toward Successful RNA Interference Therapy for Cancer Treatment
- PMID: 33973393
- PMCID: PMC8273125
- DOI: 10.1002/adhm.202100350
Innovations in Biomaterial Design toward Successful RNA Interference Therapy for Cancer Treatment
Abstract
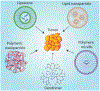
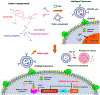
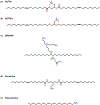
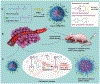
Gene regulation using RNA interference (RNAi) therapy has been developed as one of the frontiers in cancer treatment. The ability to tailor the expression of genes by delivering synthetic oligonucleotides to tumor cells has transformed the way scientists think about treating cancer. However, its clinical application has been limited due to the need to deliver synthetic RNAi oligonucleotides efficiently and effectively to target cells. Advances in nanotechnology and biomaterials have begun to address the limitations to RNAi therapeutic delivery, increasing the likelihood of RNAi therapeutics for cancer treatment in clinical settings. Herein, innovations in the design of nanocarriers for the delivery of oligonucleotides for successful RNAi therapy are discussed.
Keywords: RNA interference; biomaterials; cancer; liposomal delivery; nanomedicine; polymeric nanocarriers.
© 2021 Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Figures

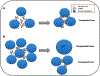
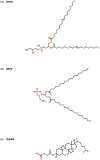
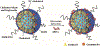

Similar articles
-
Budding Alliance of Nanotechnology in RNA Interference Therapeutics.Curr Pharm Des. 2018;24(23):2632-2643. doi: 10.2174/1381612824666180807113948. Curr Pharm Des. 2018. PMID: 30084328 Review.
-
Molecularly engineered siRNA conjugates for tumor-targeted RNAi therapy.J Control Release. 2022 Nov;351:713-726. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2022.09.040. Epub 2022 Oct 7. J Control Release. 2022. PMID: 36152808 Review.
-
Tumor-targeting multifunctional nanoparticles for siRNA delivery: recent advances in cancer therapy.Adv Healthc Mater. 2014 Aug;3(8):1182-93. doi: 10.1002/adhm.201300607. Epub 2014 Feb 28. Adv Healthc Mater. 2014. PMID: 24577795 Review.
-
Lipid-Based Nanocarriers for RNA Delivery.Curr Pharm Des. 2015;21(22):3140-7. doi: 10.2174/1381612821666150531164540. Curr Pharm Des. 2015. PMID: 26027572 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent advances in exosome-based nanovehicles as RNA interference therapeutic carriers.Nanomedicine (Lond). 2017 Nov;12(21):2653-2675. doi: 10.2217/nnm-2017-0210. Epub 2017 Sep 29. Nanomedicine (Lond). 2017. PMID: 28960165 Review.
Cited by
-
Development of Cationic Lipid LAH4-L1 siRNA Complexes for Focused Ultrasound Enhanced Tumor Uptake.Mol Pharm. 2023 May 1;20(5):2341-2351. doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.2c00909. Epub 2023 Mar 29. Mol Pharm. 2023. PMID: 36989421 Free PMC article.
-
Research progress of novel anti-tumor drug formulations.Front Oncol. 2024 Dec 16;14:1507958. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1507958. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39737395 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The infinite possibilities of RNA therapeutics.J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 2021 Dec 23;48(9-10):kuab063. doi: 10.1093/jimb/kuab063. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 34463324 Free PMC article.
-
Gel/hydrogel-based in situ biomaterial platforms for cancer postoperative treatment and recovery.Exploration (Beijing). 2023 May 31;3(5):20220173. doi: 10.1002/EXP.20220173. eCollection 2023 Oct. Exploration (Beijing). 2023. PMID: 37933278 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in siRNA Drug Delivery Strategies for Targeted TNBC Therapy.Bioengineering (Basel). 2024 Aug 14;11(8):830. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering11080830. Bioengineering (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39199788 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- WORLD HEALTH ORGANIZATION: REGIONAL OFFICE FOR EUROPE, WORLD CANCER REPORT: Cancer Research for Cancer Development., IARC, Place of Publication Not Identified, 2020.
-
- Gottesman MM, Pastan I, Annu. Rev. Biochem 1993, 62, 385. - PubMed
-
- Rupaimoole R, Slack FJ, Nat. Rev. Drug Discov 2017, 16, 203. - PubMed
-
- Yanaihara N, Caplen N, Bowman E, Seike M, Kumamoto K, Yi M, Stephens RM, Okamoto A, Yokota J, Tanaka T, et al., Cancer Cell 2006, 9, 189. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

