Ubiquitin-specific peptidase 53 inhibits the occurrence and development of clear cell renal cell carcinoma through NF-κB pathway inactivation
- PMID: 33973730
- PMCID: PMC8178486
- DOI: 10.1002/cam4.3911
Ubiquitin-specific peptidase 53 inhibits the occurrence and development of clear cell renal cell carcinoma through NF-κB pathway inactivation
Abstract
Background: Clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) is one of the most prevalent malignant diseases in the urinary system with more than 140,000 related deaths annually. Ubiquitination-deubiquitination homeostasis is an important factor in ccRCC progression; ubiquitin-specific peptidase 53 (USP53) belongs to the family of deubiquitinating enzymes, but its functions are rarely reported.
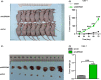
Methods: Databases obtained from GEO and TCGA were analyzed to reveal the role of USP53 in ccRCC. CCK-8/BrdU and EDU assays were used to detect the proliferation of ccRCC after USP53 overexpression or knockdown. A tumor xenograft experiment was used to verify the effect of the proliferation of ccRCC after USP53 knockdown. Transwell assays were used to detect the metastasis of ccRCC after USP53 overexpression or knockdown. RNA sequencing and western blot analysis were employed to detect the change in genes after USP53 overexpression and knockdown. Then we tested the effect of USP53 on IκBα protein stability through western blot analysis. Detect the effect of USP53 on IκBα ubiquitination in vitro by immunoprecipitation method.
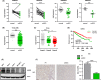
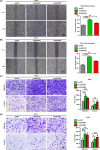
Results: USP53 expression was downregulated in ccRCC tissues and USP53 expression was significantly negatively correlated with the tumor progression and clinical prognosis. The ability of growth and metastasis of ccRCC was inhibited after USP53 overexpression. In addition, USP53 knockdown promoted ccRCC growth and metastasis. Moreover, USP53 knockdown promoted the ability of clone formation of ccRCC in vivo. NF-κB signaling pathway significantly enriched and downregulated in USP53 overexpressed cells, and genes in the NF-κB pathway (such as IL1B, CXCL1-3, RELA, RELB, etc.) were obviously downregulated in USP53 overexpressed cells. USP53 overexpression decreased the phosphorylation of IKKβ and P65 in both Caki-1 and 786-O cells, and the expression of IκBα was increased. Phosphorylation of IKKβ and P65 was increased in both Caki-1 and 786-O cells after USP53 knockdown. As the expression of USP53 increases, the protein expression of IκBα was also gradually increased and USP53 reduced the ubiquitination of IκBα.
Conclusion: In summary, our data indicate that USP53 inhibits the inactivation of the NF-κB pathway by reducing the ubiquitination of IκBα to further inhibit ccRCC proliferation and metastasis. These findings may help understand the pathogenesis of ccRCC and introduce new potential therapeutic targets for kidney cancer patients.
Keywords: NF-κB pathway; RNA sequencing; USP53; clear cell renal cell carcinoma.
© 2021 The Authors. Cancer Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures




References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J Clin 2017;67(1):7–30. - PubMed
-
- Choueiri TK, Motzer RJ. Systemic therapy for metastatic renal‐cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2017;376(4):354–366. - PubMed
-
- Srigley JR, Delahunt B, Eble JN, et al. The International Society of Urological Pathology (ISUP) Vancouver classification of renal neoplasia. Am J Surg Pathol. 2013;37(10):1469–1489. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

