The different hypoglycemic effects between East Asian and non-Asian type 2 diabetes patients when treated with SGLT-2 inhibitors as an add-on treatment for metformin: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
- PMID: 33973870
- PMCID: PMC8148508
- DOI: 10.18632/aging.202945
The different hypoglycemic effects between East Asian and non-Asian type 2 diabetes patients when treated with SGLT-2 inhibitors as an add-on treatment for metformin: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Abstract
Aims: To investigate the efficacy and safety of SGLT-2 inhibitors as an add-on treatment for metformin between Asian and non-Asian T2DM.
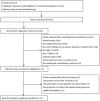
Methods: A systematic literature search of PubMed, EMBASE, and the Cochrane Library was performed through August 2020 with the following keywords: Sodium-Glucose Transporter 2 Inhibitors, Sodium Glucose Transporter 2 Inhibitors, SGLT2 inhibitor, SGLT-2 inhibitors, type 2 diabetes, and randomized controlled trials. Double-blinded RCTs comparing SGLT-2 inhibitors as an add-on treatment for metformin and metformin monotherapy in adults with type 2 diabetes were included. A random effects model was used to calculate overall effect sizes.
Results: 5 RCTs with 1193 Asian patients and 7 RCTs with 2098 non-Asian patients were investigated. The improvement in HbA1c and fasting blood glucose in the Asian patients (WMD, -0.73%; 95% CI, -1.01% to -0.46%, p < 0.01; WMD, -1.51; 95% CI, -1.81 to -1.21, p < 0.01, respectively) were both significantly better than in the non-Asians (WMD, -0.45%; 95% CI, -0.62% to -0.29%, p < 0.01; WMD, -1.03; 95% CI, -1.27 to -0.78, p < 0.01, respectively). The effect of weight loss was similar in the non-Asian patients and Asian patients. There was little difference in the improvement of systolic blood pressure between them. The risk of serious adverse events was not significantly increased between the Asian and non-Asian patients.
Conclusion: SGLT-2 inhibitors as an add-on treatment for metformin are more efficacious in East Asian T2DM patients than in non-Asian T2DM patients without an additional risk of severe adverse events.
Keywords: Asian; SGLT-2 inhibitors; meta-analysis; metformin; randomized controlled trial; type 2 diabetes.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures







References
-
- IDF. IDF DIABETES ATLAS 2019. https://www.diabetesatlas.org/en/.
-
- Buse JB, Wexler DJ, Tsapas A, Rossing P, Mingrone G, Mathieu C, D'Alessio DA, Davies MJ. 2019 Update to: Management of Hyperglycemia in Type 2 Diabetes, 2018. A Consensus Report by the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD). Diabetes Care. 2020; 43:487–93. 10.2337/dci19-0066 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

