Cbl-b deficiency prevents functional but not phenotypic T cell anergy
- PMID: 33974042
- PMCID: PMC8117209
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20202477
Cbl-b deficiency prevents functional but not phenotypic T cell anergy
Abstract
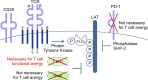
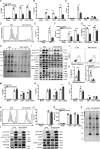
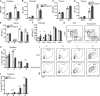
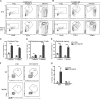
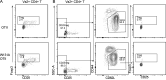
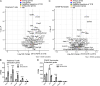
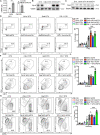
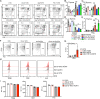
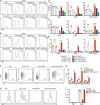
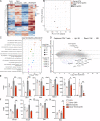
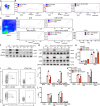
T cell anergy is an important peripheral tolerance mechanism. We studied how T cell anergy is established using an anergy model in which the Zap70 hypermorphic mutant W131A is coexpressed with the OTII TCR transgene (W131AOTII). Anergy was established in the periphery, not in the thymus. Contrary to enriched tolerance gene signatures and impaired TCR signaling in mature peripheral CD4 T cells, CD4SP thymocytes exhibited normal TCR signaling in W131AOTII mice. Importantly, the maintenance of T cell anergy in W131AOTII mice required antigen presentation via MHC-II. We investigated the functional importance of the inhibitory receptor PD-1 and the E3 ubiquitin ligases Cbl-b and Grail in this model. Deletion of each did not affect expression of phenotypic markers of anergic T cells or T reg numbers. However, deletion of Cbl-b, but not Grail or PD-1, in W131AOTII mice restored T cell responsiveness and signaling. Thus, Cbl-b plays an essential role in the establishment and/or maintenance of unresponsiveness in T cell anergy.
© 2021 Nguyen et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures: A. Weiss reported personal fees from Nurix Therapeutics and personal fees from Genentech outside the submitted work and is a co-founder of Nurix Therapeutics, a publicly traded company in which he owns stock and has received consulting fees since it was founded in 2012. Nurix is developing small molecule inhibitors of Cbl-b for use in immuno-oncology. Current inhibitors are in preclinical development. The studies performed here examine the role of Cbl-b in T cell anergy using knock out mice and find that Cbl-b is an important negative regulator of functional anergy. Neither A. Weiss, nor his lab, have had access to any small molecule inhibitors developed at Nurix. The studies reported here do not directly relate to immuno-oncology. A. Weiss is also on the Scientific Resource Board of Genentech, for which he receives financial compensation. Genentech has developed anti-PDL-1 monoclonal antibodies for use in immuno-oncology. The role of PD-1 in a mouse model of T cell anergy was studied here. Deficiency of PD-1 had no apparent effect on the model of T cell anergy studied here. No other disclosures were reported.
Figures


References
-
- Anandasabapathy, N., Ford G.S., Bloom D., Holness C., Paragas V., Seroogy C., Skrenta H., Hollenhorst M., Fathman C.G., and Soares L.. 2003. GRAIL: an E3 ubiquitin ligase that inhibits cytokine gene transcription is expressed in anergic CD4+ T cells. Immunity. 18:535–547. 10.1016/S1074-7613(03)00084-0 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Benjamini, Y., and Hochberg Y.. 1995. Controlling the False Discovery Rate - a Practical and Powerful Approach to Multiple Testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. B. 57:289–300. 10.1111/j.2517-6161.1995.tb02031.x - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

