Spliceostatins and Derivatives: Chemical Syntheses and Biological Properties of Potent Splicing Inhibitors
- PMID: 33974423
- PMCID: PMC8919379
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jnatprod.1c00100
Spliceostatins and Derivatives: Chemical Syntheses and Biological Properties of Potent Splicing Inhibitors
Abstract
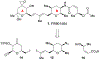
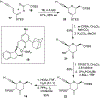
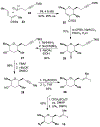
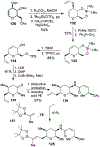
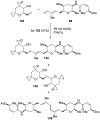
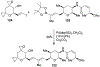
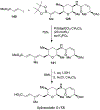
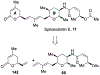
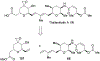
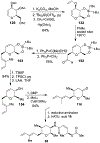
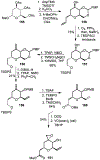
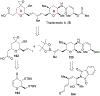
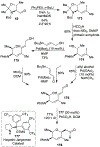
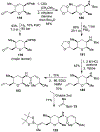
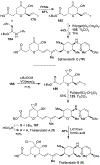
Spliceostatins and thailanstatins are intriguing natural products due to their structural features as well as their biological significance. This family of natural products has been the subject of immense synthetic interest because they exhibit very potent cytotoxicity in representative human cancer cell lines. The cytotoxic properties of these natural products are related to their ability to inhibit spliceosomes. FR901564 and spliceostatins have been shown to inhibit spliceosomes by binding to their SF3B component. Structurally, these natural products contain two highly functionalized tetrahydropyran rings with multiple stereogenic centers joined by a diene moiety and an acyclic side chain linked with an amide bond. Total syntheses of this family of natural products led to the development of useful synthetic strategies, which enabled the synthesis of potent derivatives. The spliceosome modulating properties of spliceostatins and synthetic derivatives opened the door for understanding the underlying spliceosome mechanism as well as the development of new therapies based upon small-molecule splicing modulators. This review outlines the total synthesis of spliceostatins, synthetic studies of structural derivatives, and their bioactivity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
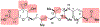













Similar articles
-
Design and synthesis of herboxidiene derivatives that potently inhibit in vitro splicing.Org Biomol Chem. 2021 Feb 18;19(6):1365-1377. doi: 10.1039/d0ob02532a. Org Biomol Chem. 2021. PMID: 33480941 Free PMC article.
-
Discoveries, target identifications, and biological applications of natural products that inhibit splicing factor 3B subunit 1.Nat Prod Rep. 2016 May 4;33(5):637-47. doi: 10.1039/c5np00110b. Nat Prod Rep. 2016. PMID: 26812544 Review.
-
Syntheses of spliceostatins and thailanstatins: a review.Beilstein J Org Chem. 2020 Aug 13;16:1991-2006. doi: 10.3762/bjoc.16.166. eCollection 2020. Beilstein J Org Chem. 2020. PMID: 32831956 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cytotoxic Spliceostatins from Burkholderia sp. and Their Semisynthetic Analogues.J Nat Prod. 2014 Aug 22;77(8):1864-70. doi: 10.1021/np500342m. J Nat Prod. 2014. PMID: 25098528
-
Total Synthesis of Thailanstatin A.J Am Chem Soc. 2016 Jun 22;138(24):7532-5. doi: 10.1021/jacs.6b04781. Epub 2016 Jun 13. J Am Chem Soc. 2016. PMID: 27266914
Cited by
-
Stereochemical Control of Splice Modulation in FD-895 Analogues.J Med Chem. 2023 May 25;66(10):6577-6590. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.2c01893. Epub 2023 May 8. J Med Chem. 2023. PMID: 37155693 Free PMC article.
-
Small molecules modulating RNA splicing: a review of targets and future perspectives.RSC Med Chem. 2024 Jan 11;15(4):1109-1126. doi: 10.1039/d3md00685a. eCollection 2024 Apr 24. RSC Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 38665842 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent updates and future perspectives in aziridine synthesis and reactivity.Chem. 2023 Jul 13;9(7):1658-1701. doi: 10.1016/j.chempr.2023.04.010. Epub 2023 May 11. Chem. 2023. PMID: 37681216 Free PMC article.
-
Structural insights into branch site proofreading by human spliceosome.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2024 May;31(5):835-845. doi: 10.1038/s41594-023-01188-0. Epub 2024 Jan 9. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 38196034
-
The Evolving Landscape of Antibody-Drug Conjugates: In Depth Analysis of Recent Research Progress.Bioconjug Chem. 2023 Nov 15;34(11):1951-2000. doi: 10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.3c00374. Epub 2023 Oct 11. Bioconjug Chem. 2023. PMID: 37821099 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Newman DJ; Cragg GW Natural Products as Sources of New Drugs over the Nearly Four Decades from 01/1981 to 09/2019 J. Nat. Prod 2020, 83, 770–803. - PubMed
-
- Newman DJ; Cragg GM J. Nat. Prod 2007, 70 (3), 461–477. - PubMed
-
- Haustedt LO; Mang C; Siems K; Schiewe H Curr. Opin. Drug Discovery Dev 2006, 9 (4), 445–462. - PubMed
-
- Maier ME Org. Biomol. Chem 2015, 13 (19), 5302–5343. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

