A simple criterion to design optimal non-pharmaceutical interventions for mitigating epidemic outbreaks
- PMID: 33975462
- PMCID: PMC8113910
- DOI: 10.1098/rsif.2020.0803
A simple criterion to design optimal non-pharmaceutical interventions for mitigating epidemic outbreaks
Abstract
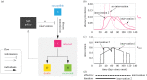
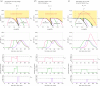
For mitigating the COVID-19 pandemic, much emphasis is made on implementing non-pharmaceutical interventions to keep the reproduction number below one. However, using that objective ignores that some of these interventions, like bans of public events or lockdowns, must be transitory and as short as possible because of their significant economic and societal costs. Here, we derive a simple and mathematically rigorous criterion for designing optimal transitory non-pharmaceutical interventions for mitigating epidemic outbreaks. We find that reducing the reproduction number below one is sufficient but not necessary. Instead, our criterion prescribes the required reduction in the reproduction number according to the desired maximum of disease prevalence and the maximum decrease of disease transmission that the interventions can achieve. We study the implications of our theoretical results for designing non-pharmaceutical interventions in 16 cities and regions during the COVID-19 pandemic. In particular, we estimate the minimal reduction of each region's contact rate necessary to control the epidemic optimally. Our results contribute to establishing a rigorous methodology to design optimal non-pharmaceutical intervention policies for mitigating epidemic outbreaks.
Keywords: COVID-19; epidemic outbreak; non-pharmaceutical interventions; optimal control.
Figures



References
-
- Anderson RM, May RM. 1992. Infectious diseases of humans: dynamics and control. Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press.
-
- Kupferschmidt K. 2020. Ending coronavirus lockdowns will be a dangerous process of trial and error. Science—AAAS. (10.1126/science.abc2507) - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
