CBR3 V244M is associated with LVEF reduction in breast cancer patients treated with doxorubicin
- PMID: 33975650
- PMCID: PMC8111996
- DOI: 10.1186/s40959-021-00103-0
CBR3 V244M is associated with LVEF reduction in breast cancer patients treated with doxorubicin
Abstract
Background: The CBR3 V244M single nucleotide polymorphism has been linked to the risk of anthracycline-related cardiomyopathy in survivors of childhood cancer. There have been limited prospective studies examining the impact of CBR3 V244M on the risk for anthracycline-related cardiotoxicity in adult cohorts.
Objectives: This study evaluated the presence of associations between CBR3 V244M genotype status and changes in echocardiographic parameters in breast cancer patients undergoing doxorubicin treatment.
Methods: We recruited 155 patients with breast cancer receiving treatment with doxorubicin (DOX) at Roswell Park Comprehensive Care Center (Buffalo, NY) to a prospective single arm observational pharmacogenetic study. Patients were genotyped for the CBR3 V244M variant. 92 patients received an echocardiogram at baseline (t0 month) and at 6 months (t6 months) of follow up after DOX treatment. Apical two-chamber and four-chamber echocardiographic images were used to calculate volumes and left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) using Simpson's biplane rule by investigators blinded to all patient data. Volumetric indices were evaluated by normalizing the cardiac volumes to the body surface area (BSA).
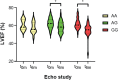
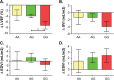
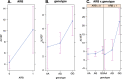
Results: Breast cancer patients with CBR3 GG and AG genotypes both experienced a statistically significant reduction in LVEF at 6 months following initiation of DOX treatment for breast cancer compared with their pre-DOX baseline study. Patients homozygous for the CBR3 V244M G allele (CBR3 V244) exhibited a further statistically significant decrease in LVEF at 6 months following DOX therapy in comparison with patients with heterozygous AG genotype. We found no differences in age, pre-existing cardiac diseases associated with myocardial injury, cumulative DOX dose, or concurrent use of cardioprotective medication between CBR3 genotype groups.
Conclusions: CBR3 V244M genotype status is associated with changes in echocardiographic parameters suggestive of early anthracycline-related cardiomyopathy in subjects undergoing chemotherapy for breast cancer.
Keywords: Anthracycline; Breast Cancer; Carbonyl Reductase 3; Cardiotoxicity; Cardiovascular disease; Chemotherapy; Doxorubicin; Survivorship.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Blanco JG, Sun CL, Landier W, Chen L, Esparza-Duran D, Leisenring W, Mays A, Friedman DL, Ginsberg JP, Hudson MM, Neglia JP, Oeffinger KC, Ritchey AK, Villaluna D, Relling MV, Bhatia S. Anthracycline-related cardiomyopathy after childhood cancer: role of polymorphisms in carbonyl reductase genes--a report from the Children's oncology group. J Clin Oncol. 2012;30(13):1415–1421. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2011.34.8987. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Subset Selection in Regression By Alan Miller 2nd Edition. Chapman and Hall/CRC; 2002. p. 256. Published September 5, 2019.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
