Phase separation of EML4-ALK in firing downstream signaling and promoting lung tumorigenesis
- PMID: 33976114
- PMCID: PMC8113584
- DOI: 10.1038/s41421-021-00270-5
Phase separation of EML4-ALK in firing downstream signaling and promoting lung tumorigenesis
Abstract
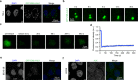
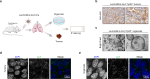
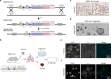
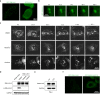
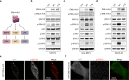
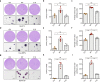
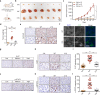
EML4-ALK fusion, observed in about 3%-7% of human lung adenocarcinoma, is one of the most important oncogenic drivers in initiating lung tumorigenesis. However, it still remains largely unknown about how EML4-ALK fusion exactly fires downstream signaling and drives lung cancer formation. We here find that EML4-ALK variant 1 (exon 1-13 of EML4 fused to exon 20-29 of ALK) forms condensates via phase separation in the cytoplasm of various human cancer cell lines. Using two genetically engineered mouse models (GEMMs), we find that EML4-ALK variant 1 can drive lung tumorigenesis and these murine tumors, as well as primary tumor-derived organoids, clearly show the condensates of EML4-ALK protein, further supporting the findings from in vitro study. Mutation of multiple aromatic residues in EML4 region significantly impairs the phase separation of EML4-ALK and dampens the activation of the downstream signaling pathways, especially the STAT3 phosphorylation. Importantly, it also significantly decreases cancer malignant transformation and tumor formation. These data together highlight an important role of phase separation in orchestrating EML4-ALK signaling and promoting tumorigenesis, which might provide new clues for the development of clinical therapeutic strategies in treating lung cancer patients with the EML4-ALK fusion.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Role of ERK-BIM and STAT3-survivin signaling pathways in ALK inhibitor-induced apoptosis in EML4-ALK-positive lung cancer.Clin Cancer Res. 2011 Apr 15;17(8):2140-8. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-2798. Epub 2011 Mar 17. Clin Cancer Res. 2011. PMID: 21415216
-
Effects of SMYD2-mediated EML4-ALK methylation on the signaling pathway and growth in non-small-cell lung cancer cells.Cancer Sci. 2017 Jun;108(6):1203-1209. doi: 10.1111/cas.13245. Cancer Sci. 2017. PMID: 28370702 Free PMC article.
-
A new human lung adenocarcinoma cell line harboring the EML4-ALK fusion gene.Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2014 Oct;44(10):963-8. doi: 10.1093/jjco/hyu110. Epub 2014 Aug 28. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2014. PMID: 25170107
-
Going beneath the tip of the iceberg. Identifying and understanding EML4-ALK variants and TP53 mutations to optimize treatment of ALK fusion positive (ALK+) NSCLC.Lung Cancer. 2021 Aug;158:126-136. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2021.06.012. Epub 2021 Jun 12. Lung Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34175504 Review.
-
[A new target in non-small cell lung cancer: EML4-ALK fusion gene].Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2011 Jun;14(6):538-42. doi: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2011.06.11. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2011. PMID: 21645460 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Biomolecular condensates and disease pathogenesis.Sci China Life Sci. 2024 Sep;67(9):1792-1832. doi: 10.1007/s11427-024-2661-3. Epub 2024 Jul 17. Sci China Life Sci. 2024. PMID: 39037698 Review.
-
Liquid-liquid phase separation: a new perspective on respiratory diseases.Front Immunol. 2024 Sep 26;15:1444253. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1444253. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39391315 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interleukin-6 at the Host-Tumor Interface: STAT3 in Biomolecular Condensates in Cancer Cells.Cells. 2022 Mar 30;11(7):1164. doi: 10.3390/cells11071164. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35406728 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular features driving condensate formation and gene expression by the BRD4-NUT fusion oncoprotein are overlapping but distinct.Sci Rep. 2023 Jul 24;13(1):11907. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-39102-9. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37488172 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of Phase-Separated Biomolecular Condensates in Cancer.Methods Mol Biol. 2023;2660:345-356. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-3163-8_23. Methods Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 37191808 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

