Neural network aided approximation and parameter inference of non-Markovian models of gene expression
- PMID: 33976195
- PMCID: PMC8113478
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-021-22919-1
Neural network aided approximation and parameter inference of non-Markovian models of gene expression
Abstract
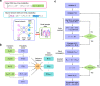
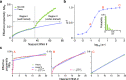
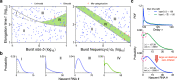
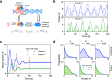
Non-Markovian models of stochastic biochemical kinetics often incorporate explicit time delays to effectively model large numbers of intermediate biochemical processes. Analysis and simulation of these models, as well as the inference of their parameters from data, are fraught with difficulties because the dynamics depends on the system's history. Here we use an artificial neural network to approximate the time-dependent distributions of non-Markovian models by the solutions of much simpler time-inhomogeneous Markovian models; the approximation does not increase the dimensionality of the model and simultaneously leads to inference of the kinetic parameters. The training of the neural network uses a relatively small set of noisy measurements generated by experimental data or stochastic simulations of the non-Markovian model. We show using a variety of models, where the delays stem from transcriptional processes and feedback control, that the Markovian models learnt by the neural network accurately reflect the stochastic dynamics across parameter space.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Periodic synchronization of isolated network elements facilitates simulating and inferring gene regulatory networks including stochastic molecular kinetics.BMC Bioinformatics. 2022 Jan 5;23(1):13. doi: 10.1186/s12859-021-04541-6. BMC Bioinformatics. 2022. PMID: 34986805 Free PMC article.
-
Holimap: an accurate and efficient method for solving stochastic gene network dynamics.Nat Commun. 2024 Aug 2;15(1):6557. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-50716-z. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39095346 Free PMC article.
-
Analytical results for non-Markovian models of bursty gene expression.Phys Rev E. 2020 May;101(5-1):052406. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.101.052406. Phys Rev E. 2020. PMID: 32575237
-
Stochastic and delayed stochastic models of gene expression and regulation.Math Biosci. 2010 Jan;223(1):1-11. doi: 10.1016/j.mbs.2009.10.007. Epub 2009 Oct 31. Math Biosci. 2010. PMID: 19883665 Review.
-
Stochastic Modeling of Autoregulatory Genetic Feedback Loops: A Review and Comparative Study.Biophys J. 2020 Apr 7;118(7):1517-1525. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2020.02.016. Epub 2020 Feb 25. Biophys J. 2020. PMID: 32155410 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Learning of Iterative Learning Control for Flexible Manufacturing of Batch Processes.ACS Omega. 2022 May 30;7(23):19939-19947. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.2c01741. eCollection 2022 Jun 14. ACS Omega. 2022. PMID: 35721960 Free PMC article.
-
Inference and uncertainty quantification of stochastic gene expression via synthetic models.J R Soc Interface. 2022 Jul;19(192):20220153. doi: 10.1098/rsif.2022.0153. Epub 2022 Jul 13. J R Soc Interface. 2022. PMID: 35858045 Free PMC article.
-
Intelligent system for human activity recognition in IoT environment.Complex Intell Systems. 2021 Sep 7:1-12. doi: 10.1007/s40747-021-00508-5. Online ahead of print. Complex Intell Systems. 2021. PMID: 34777979 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic Batch Process Monitoring Based on Time-Slice Latent Variable Correlation Analysis.ACS Omega. 2022 Oct 31;7(45):41069-41081. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.2c04445. eCollection 2022 Nov 15. ACS Omega. 2022. PMID: 36406484 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of noise and time delay on E2F's expression level in a bistable Rb-E2F gene's regulatory network.IET Syst Biol. 2021 Jun;15(4):111-125. doi: 10.1049/syb2.12017. Epub 2021 Apr 21. IET Syst Biol. 2021. PMID: 33881232 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Peccoud J, Ycart B. Markovian modeling of gene-product synthesis. Theor. Popul. Biol. 1995;48:222–234. doi: 10.1006/tpbi.1995.1027. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

