Proteome and transcriptome analyses of wheat near isogenic lines identifies key proteins and genes of wheat bread quality
- PMID: 33976249
- PMCID: PMC8113351
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-89140-4
Proteome and transcriptome analyses of wheat near isogenic lines identifies key proteins and genes of wheat bread quality
Abstract
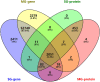
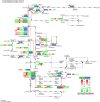
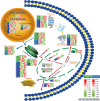
The regulation of wheat protein quality is a highly complex biological process involving multiple metabolic pathways. To reveal new insights into the regulatory pathways of wheat glutenin synthesis, we used the grain-filling period wheat grains of the near-isogenic lines NIL-723 and NIL-1010, which have large differences in quality, to perform a combined transcriptome and proteome analysis. Compared with NIL-1010, NIL-723 had 1287 transcripts and 355 proteins with significantly different abundances. Certain key significantly enriched pathway were identified, and wheat quality was associated with alanine, aspartate and glutamate metabolism, nitrogen metabolism and alpha-linolenic acid metabolism. Differentially expressed proteins (DEPs) or Differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in amino acid synthesis pathways were upregulated primarily in the glycine (Gly), methionine (Met), threonine (Thr), glutamic acid (Glu), proline (proC), cysteine (Cys), and arginine (Arg) synthesis and downregulated in the tryptophan (trpE), leucine (leuC), citrulline (argE), and ornithine (argE) synthesis. Furthermore, to elucidate changes in glutenin in the grain synthesis pathway, we plotted a regulatory pathway map and found that DEGs and DEPs in ribosomes (RPL5) and the ER (HSPA5, HYOU1, PDIA3, PDIA1, Sec24, and Sec31) may play key roles in regulating glutenin synthesis. The transcriptional validation of some of the differentially expressed proteins through real-time quantitative PCR analysis further validated the transcriptome and proteomic results.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Comparative proteome analysis of glutenin synthesis and accumulation in developing grains between superior and poor quality bread wheat cultivars.J Sci Food Agric. 2012 Jan 15;92(1):106-15. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.4548. Epub 2011 Aug 4. J Sci Food Agric. 2012. PMID: 21815156
-
Composition and functional analysis of low-molecular-weight glutenin alleles with Aroona near-isogenic lines of bread wheat.BMC Plant Biol. 2012 Dec 22;12:243. doi: 10.1186/1471-2229-12-243. BMC Plant Biol. 2012. PMID: 23259617 Free PMC article.
-
Deletion of the low-molecular-weight glutenin subunit allele Glu-A3a of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) significantly reduces dough strength and breadmaking quality.BMC Plant Biol. 2014 Dec 19;14:367. doi: 10.1186/s12870-014-0367-3. BMC Plant Biol. 2014. PMID: 25524150 Free PMC article.
-
Novel insights into the effect of nitrogen on storage protein biosynthesis and protein body development in wheat caryopsis.J Exp Bot. 2017 Apr 1;68(9):2259-2274. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erx108. J Exp Bot. 2017. PMID: 28472326
-
Absence of Dx2 at Glu-D1 Locus Weakens Gluten Quality Potentially Regulated by Expression of Nitrogen Metabolism Enzymes and Glutenin-Related Genes in Wheat.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Feb 18;21(4):1383. doi: 10.3390/ijms21041383. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32085665 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Accelerating crop improvement via integration of transcriptome-based network biology and genome editing.Planta. 2025 Mar 17;261(4):92. doi: 10.1007/s00425-025-04666-5. Planta. 2025. PMID: 40095140 Review.
-
Consensus genomic regions associated with grain protein content in hexaploid and tetraploid wheat.Front Genet. 2022 Sep 28;13:1021180. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.1021180. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 36246648 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome and Proteome Analysis Revealed the Influence of High-Molecular-Weight Glutenin Subunits (HMW-GSs) Deficiency on Expression of Storage Substances and the Potential Regulatory Mechanism of HMW-GSs.Foods. 2023 Jan 12;12(2):361. doi: 10.3390/foods12020361. Foods. 2023. PMID: 36673453 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Noorfarahzilah M, et al. Applications of composite flour in development of food products. Int. Food Res. J. 2014;21(6):2061–2074.
-
- Wang P, Jin ZY, Xu XM. Physicochemical alterations of wheat gluten proteins upon dough formation and frozen storage- A review from gluten, glutenin and gliadin perspectives. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2015;46(2):189–198. doi: 10.1016/j.tifs.2015.10.005. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

