A systematic review and meta-analysis of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor use and psoriasis incidence
- PMID: 33976340
- PMCID: PMC8113539
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-89490-z
A systematic review and meta-analysis of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor use and psoriasis incidence
Abstract
Although a considerable volume of data supporting induction or aggravation of psoriasis because of angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor use exists, it remains insufficient for definitive conclusions. Therefore, we aimed to evaluate the association between ACE inhibitor use and psoriasis incidence through a systematic literature review and meta-analysis. We searched for qualifying studies across PubMed, Web of Science, and Embase. Odds ratios (ORs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were calculated to evaluate the strength of the association between ACE inhibitor use and psoriasis incidence. Eight studies with a total of 54,509 patients with a psoriasis diagnosis were included in this meta-analysis. The pooled OR for psoriasis incidence among ACE inhibitor users was 1.52 (95% CI, 1.16-2.00) compared to that among non-users. From subgroup analysis by continent, the OR for ACE inhibitor users versus non-users was 2.37 (95% CI 1.28-4.37) in Asia. Per the subgroup analysis by climate, the OR for ACE inhibitor users vs non-users in dry climate was 3.45 (95% CI: 2.05-5.79) vs 1.32 (95% CI 1.01-1.73) in temperate climate. Our results reveal a significant association between ACE inhibitor use and psoriasis incidence.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
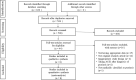



Similar articles
-
Psoriasis associated with ACE inhibitors: an analysis of the FAERS database.Pharmazie. 2020 Oct 1;75(10):524-526. doi: 10.1691/ph.2020.0606. Pharmazie. 2020. PMID: 33305730
-
A Systematic Review of Outcomes Associated With Withholding or Continuing Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors and Angiotensin Receptor Blockers Before Noncardiac Surgery.Anesth Analg. 2018 Sep;127(3):678-687. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0000000000002837. Anesth Analg. 2018. PMID: 29381513
-
Angiotensin-converting enzyme insertion/deletion polymorphism and gastric cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015 Apr 15;8(4):5788-93. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015. PMID: 26131166 Free PMC article.
-
ACE inhibitors and the risk of fractures: a meta-analysis of observational studies.Endocrine. 2017 Mar;55(3):732-740. doi: 10.1007/s12020-016-1201-5. Epub 2016 Dec 19. Endocrine. 2017. PMID: 27995498
-
The angiotensin-converting enzyme insertion/deletion polymorphism and susceptibility to rheumatoid arthritis, vitiligo and psoriasis: A meta-analysis.J Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst. 2015 Mar;16(1):195-202. doi: 10.1177/1470320313478285. Epub 2013 Feb 14. J Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst. 2015. PMID: 23413281 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification and Characterization of Novel ACE Inhibitory and Antioxidant Peptides from Sardina pilchardus Hydrolysate.Foods. 2023 May 31;12(11):2216. doi: 10.3390/foods12112216. Foods. 2023. PMID: 37297461 Free PMC article.
-
Delayed drug-induced liver injury (DILI) and flare of chronic plaque psoriasis secondary to lisinopril use.BMJ Case Rep. 2024 Jan 23;17(1):e256317. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2023-256317. BMJ Case Rep. 2024. PMID: 38262719
-
Drug-related psoriasis.Postepy Dermatol Alergol. 2023 Jun;40(3):470-471. doi: 10.5114/ada.2022.124418. Epub 2023 Jan 25. Postepy Dermatol Alergol. 2023. PMID: 37545815 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
The Renin-Angiotensin System: The Challenge behind Autoimmune Dermatological Diseases.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Nov 7;13(22):3398. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13223398. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37998534 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pharmacotherapy of arterial hypertension in patients with psoriasis.J Hypertens. 2025 Apr 1;43(4):568-576. doi: 10.1097/HJH.0000000000003982. Epub 2025 Feb 17. J Hypertens. 2025. PMID: 39976197 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

