COVID-19 and elective joint arthroplasty: Patient perspectives and considerations
- PMID: 33976477
- PMCID: PMC8102437
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jor.2021.05.009
COVID-19 and elective joint arthroplasty: Patient perspectives and considerations
Abstract
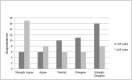
This study gauged patient perspectives regarding elective joint arthroplasty during the COVID-19 pandemic. Eligible patients undergoing consultation for primary hip or knee arthroplasty received a survey with questions regarding opinions towards COVID-19 and on undergoing elective procedures during the pandemic. Of the 112 respondents, 78% believed that their condition warranted surgery despite COVID-19 circumstances. There were no differences in desire for surgery based on age, smoking history or comorbidities. Patients older than 65 years were significantly more concerned with skilled nursing facility placement. This survey suggests that the majority of patients are comfortable pursuing elective joint arthroplasty despite the pandemic.
Keywords: COVID-19; Elective surgery; Patient perspective; Total joint arthroplasty.
© 2021 Published by Elsevier B.V. on behalf of Professor P K Surendran Memorial Education Foundation.
Conflict of interest statement
None. This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Figures
References
-
- Kurtz S.M., Ong K.L., Lau E., Bozic K.J. Impact of the economic downturn on total joint replacement demand in the United States: updated projections to 2021. JBJS. 2014;96(8) - PubMed
-
- Worldometers.info. United States Coronavirus Cases. Accessed July 26, 2020. https://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus/country/us/.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources